Which wire to use for grounding
Briefly about the terms
To make the article understandable even for those who are far from electrical engineering, we have provided an explanation of the terms that will be used in it.
The earthing switch is the basis of the grounding system. Usually it is a metal pin driven into the ground at an equal distance from each other, forming a figure like a triangle.
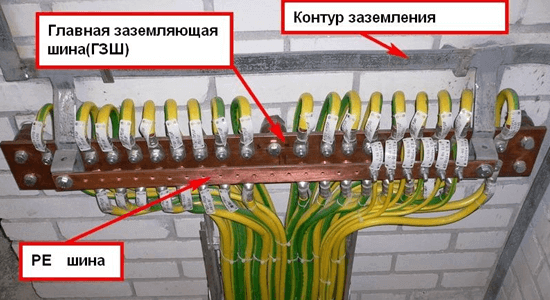
Grounding bus or Gzsh they call a metal strip laid around the perimeter of the room or near protected devices, which connects all the grounding conductors of electrical appliances to the ground electrode.
A grounding wire or a residential wire is called that conductor that provides the connection of the ground electrode to the GZSH.
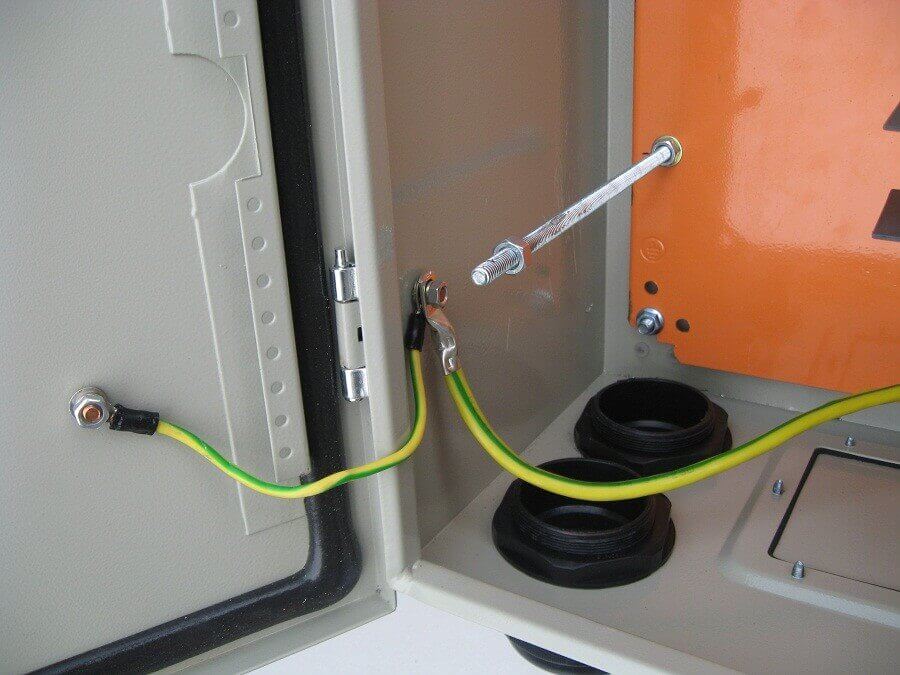
Metal communication is a concept that characterizes the contact between the metal parts of the enclosures of electrical equipment, including the doors of electrical panels or cabinets with their enclosures.
Ground wire cross section
To ensure reliable protection against electric shock and the operation of protective switching devices, the ground wire is selected depending on the phase cross section. This is necessary so that in case of an accident it can withstand high currents and not burn out. If this happens, then the protection will not work, and the dangerous potential will be on the body of the appliance.
The cross section of the ground wire should be:
- If the phase is used with a cross section up to 16 square meters. mm - the grounding conductor should be the same size.
- If the phase cross-sectional area is from 16 to 35 square meters. mm, then the "land" it should be 16 square meters. mm
- With a phase cross section greater than 35 square meters. mm - the minimum cross-section of the ground wire must be at least half the phase cross-section.
We give two examples to answer the question of what section should be at the grounding of the device:
- You connect the electric stove with a cable with a cross section of 4 sq. mm So the cross-section of the protective wire should be the same.
- An input cable is connected to the electrical cabinet with conductors of 50 sq. mm In this case, the cross-section of the ground must be at least 25 square meters. mm You can do more.
Brand and requirements for conductors
The conductor of the grounding wire or cable can be both single-core and multi-core - it depends only on where it will be used. For example, to ground the door in the electrical panel, you must ensure its mobility. A rigid core from constant opening of the door and its bending will fracture.Therefore, the core must have an appropriate class of flexibility that does not preclude opening, for example 3 and above.
At the same time, for connecting, for example, the motor housing of the pumping station to the GZSH, it is not necessary to provide mobility, since this type of electrical equipment is permanently mounted. Therefore, you can use hard cores.
Earth conductor can be:
- isolated;
- uninsulated;
- is part of the cable;
- be a separate solid wire;
- aluminum;
- copper.
This begs the question: so which wire should I use to connect the earth?
Cable products with different number of cores are sold in stores: 2, 3, 4, 5. This is necessary for assembling certain schemes for switching on devices and connecting electrical equipment to networks with different numbers of phases.
To connect the ground in sockets and other electrical equipment of a single-phase network, it is convenient to use three-core cables, for example VVG 3x2.5. And for connecting three-phase equipment to the network and grounding, four-core cables, for example AVVG 4x32, are intended. Moreover, in thick cables, the grounding conductor usually has a cross section smaller than that of phase conductors. Here are some examples.
Cables:
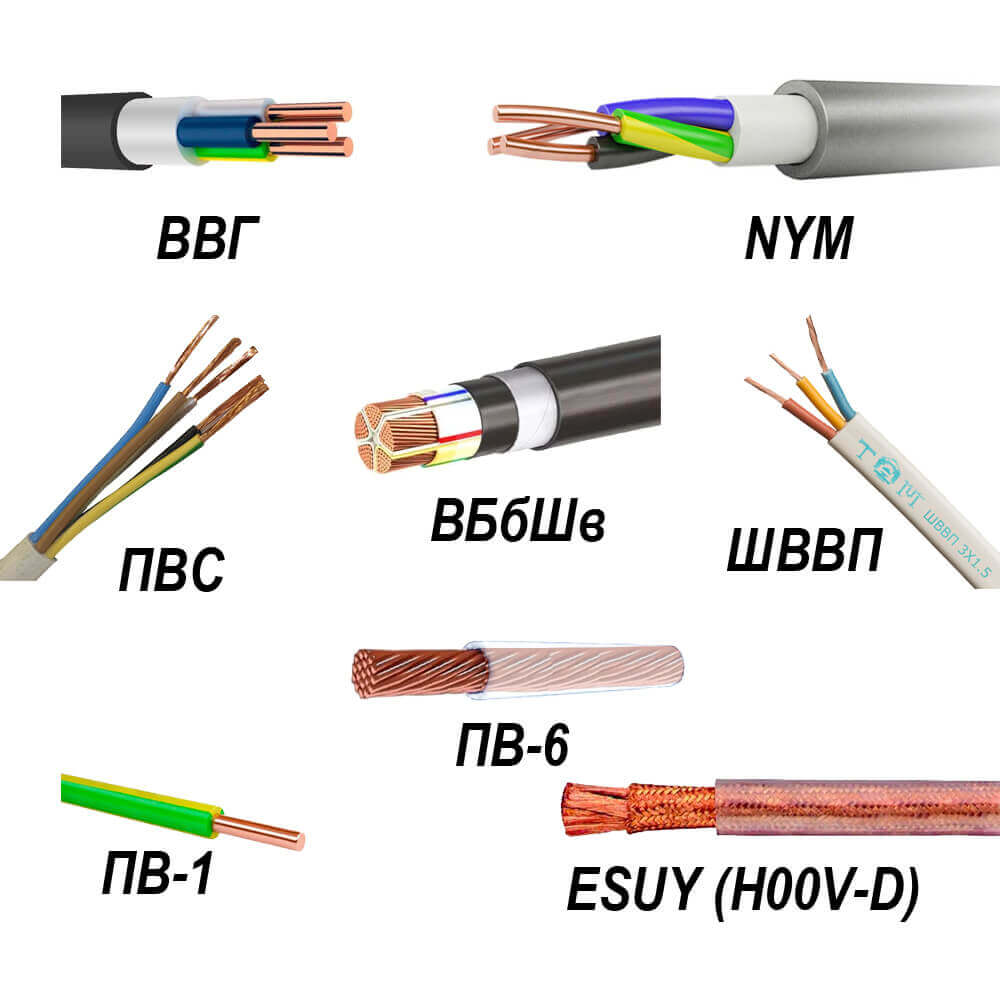
- VVG - suitable for indoor use. For laying on the street it must be placed in corrugation or pipes. It is produced with a different number of cores; there is a more detailed overview of this cable on the site. For use in hot rooms it is better to use VVGng-ls. This cable is stiff and better suited for fixed installation.
- NYM - A foreign brand is similar in characteristics to VVG. Hard.
- VBBSHV - Suitable for outdoor use and digging in a trench, often used to connect a private house to the network. Hard.
Wires:
- PVA - Well suited for connecting power tools and extension cords, because it consists of multi-wire flexible cores. It is produced in two and three-core version.
- Ball screw - similar to the previous one, only it is not round, but flat.
- ESUY - single core soft copper wire.
To connect the ground wire to the plumbing and other things in the bath, you can use single-core wires marked with PV. The number after these letters indicates the flexibility class, where PV-1 hard core, and PV-4 or PV-6 multi-wire flexible core.
Wire color and connection features
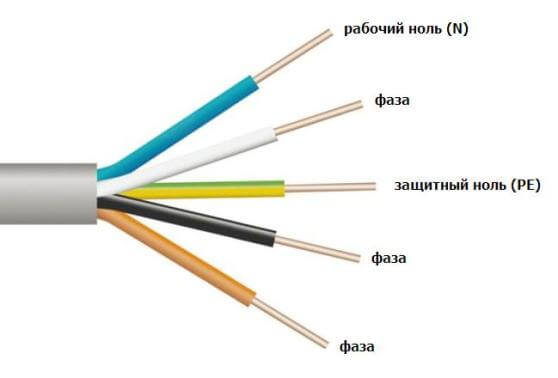
What color should the ground wire insulation be? Grounding conductors and busbars always have a yellow-green striped color. This allows you to accurately (if the installation is correct) determine the purpose of the wires when repairing wiring. The phase conductor can be brown or another color, and the zero is almost always blue. In DC circuits, they often mark red plus and black minus. This issue is considered in more detail in the article: wire color marking.
If you got a cable with a color marking that does not comply with GOSTs, you can mark the earth, phase and zero with an electrical tape or heat-shrink tube. In addition to color coding, there is also a letter or number:
- L - Line or phase.
- N - Neutral or neutral, zero.
- PEN or PE - protective conductor or ground.
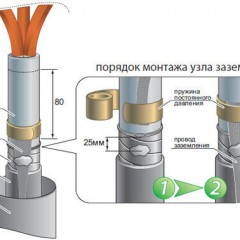
For connection in the input and distribution panel (and other places) often use earth and zero tires. This is a rail with a set of holes and screw clamps, where the wires are connected. To connect a ground wire with a multi-wire core, it is necessary to irradiate or crimp with a pin tip NSHVI and the like. This rule also applies to connecting to terminals of automatic machines and other screw connections of any flexible conductors.
To connect the wire to the grounding bus, it is necessary to use the round terminals of NKI, NVI or other types of cable lugs with terminals in the form of a ring.
This may be required when grounding from the loop to the shield. Usually they are of two types:
- Crimp. In order to fix them on the cable they are crimped with a special tool. You should not do this with pliers, because you will not achieve a reliable crimp.The best compression is provided by press tongs (another name is crimper) with hexagonal (hexagonal) clamps.
- With stall screws - to tighten them just tighten the screw until its head breaks.
That's all we wanted to tell you in this article. Now you know what section and brand the wire should be for grounding. Finally, we recommend watching a useful video on the topic:
Related materials:









Is it necessary to ground the door from a metal electrical panel?
thanks in advance,
Mandatory.
Hello.
And with what section of the copper wire do you need to ground the shield door or suppose the KTP door ????
in the article in the section on "Cross-section of the ground wire" typical values are given!
when considering p.
is it possible to make a ground loop in 30-40 meters about the house (there is the wettest place)
The PUE has a paragraph 1.7.90, where it is said that the minimum distance is 0.8-1 meters for longitudinal earthing switches, and this distance is optimal. How are you going to lay these 30-40 meters? if a steel strip is buried in the ground, we can still talk about efficiency, since it will play the role of a longitudinal ground electrode, but we must not forget about the line resistance and the fact that it reduces the efficiency of the circuit. The shorter and thicker the ground conductor the better.
It is better to make a ground electrode system with a large number and long pins near the house than to rely on soil moisture.
Tell me please. I have a 2.5 square copper wire socket. Grounding is not in it. Is it possible to throw from a nearby outlet via an Internet cable. twisting all the ends tightly?
The internet cable cannot be grounded. It has a low section. With a short circuit current, it may ignite.