How to lay the cable in an explosive room
Cable requirements
An explosive facility requires the use of a certain type of cable product. The danger zone can be of a different class, but the conductor must have a certain shell, namely:
- paper and rubber insulation;
- polyvinyl chloride and rubber insulation (used in water and gas pipelines);
- rubber and lead sheath (also used in water and gas pipelines).
Explosive areas are classified in the chapter. 7.3 PUE. An explosive facility, regardless of the hazard class, does not allow the use of wiring with polyethylene insulation.
The zone of class B1 and B1a is dangerous, therefore the cable line is used with copper conductors. To lay the network in zones B16, B1g, B11 and B1a, a cable with aluminum conductors and aluminum insulation is used. It is strictly forbidden to use bare wires in such areas.
Classification of hazardous objects:
As for suitable grades of cable for installation in hazardous areas, these include VBBSHV, KVBBSHV, KPGN, VBV and ABBV.
Cable routing methods
How to lay the cable in hazardous areas? There are several options for laying and these options are recommended by the PUE. For example, in electric networks with voltage up to 1 kV, for grounding or grounding use a separate cable core. In this case, the armor (metal sheath) of the cable is earthed from both sides (at the beginning and end of the line), according to the chapter 2.3. PUE Sec. 2.3.71, 72, and also chapter 1.7, for example, n. 1.7.97, 98 and a number of other of these chapters.
At explosive facilities in which the hazard zone belongs to class B1 and B1a, the cable line is laid in pipes, which, in turn, are located in the wall. The end of the pipe is processed and sealed with special pipe glands.
Installation of electrical wiring in the place where the explosive object passes into a normal room is carried out as follows: pipe glands are installed on the side of the room where the explosion hazard zone has a large class. If laying is carried out between rooms where the explosive class is the same, then the pipe glands must be placed in the building where the mixtures of a higher category are located. If hazard class B1, then glands should be placed on both sides of the aisle.
It's important to know! The cable line that needs to be laid through the floors should go 0.15 meters from the floor surface.
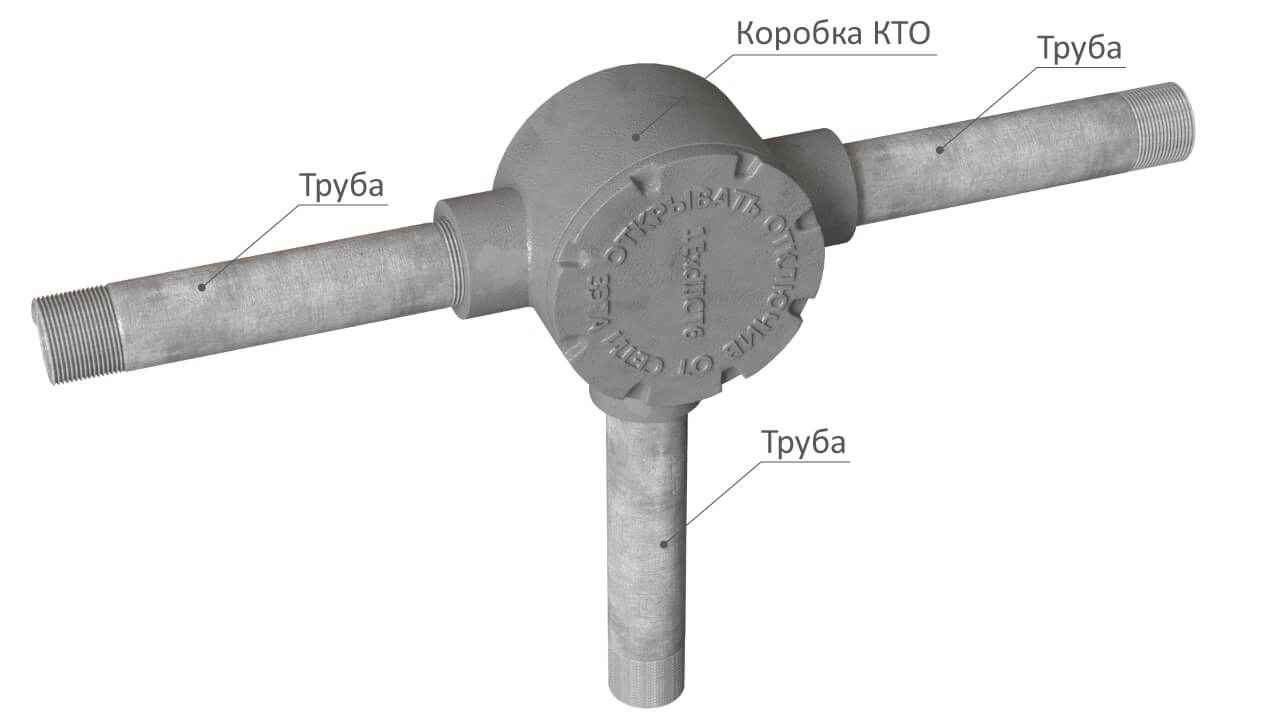
In order to protect the cable from various mechanical or chemical damage, it is placed in metal pipes. In the pipe, the cable line is under reliable protection. With the help of cast-iron boxes, type B (so-called fittings), which are sufficiently protected from explosions, cable lines are connected and branched. The photo below shows the appearance of the explosion-proof box:
If laying is carried out in a room with increased dampness, then the cable is laid with a certain bias to the broaching as well as junction boxes. If the area where it is necessary to lay the cable has excessive moisture, then the wiring is laid with the direction to the catchment pipe. If the room is dry, then this method of laying is not needed, but if condensation can occur, then a bias should be made in the direction where it is expected to fall out.
The danger zone implies a different class of object, which also determines the method by which the cable can be laid. If the circuit is intrinsically safe, then the gasket can be carried out both open and closed. If the explosive object belongs to class B2, then laying is carried out using special trays. In addition, it should be remembered that if the wiring is armored, then it is necessary to use structures in which horizontal surfaces are narrow. They are also placed on the edge and the distance to the wall should be from 20 millimeters.
It's important to know! All these measures are necessary in order to protect the room from the possible occurrence of explosive dust, which is quite difficult to remove.
Lay the cable in explosive atmospheres so that the wiring is not damaged. In addition, it is necessary that the cable lines themselves are tight and well protected from explosions, because conductors can be sources of ignition of combustible substances. The area where combustible substances are located is considered to be explosive and one spark is enough to cause a fire. That is why it is necessary to strictly observe and adhere to existing safety rules and requirements. If all the requirements are met and the rules are followed, then the occurrence of an emergency is minimized.
So we examined how the cable should be laid in hazardous areas. For a more detailed consideration of the issue, we recommend that you study such regulatory documents as the PUE (chapter 7.3) and GOST R 51330.13-99 (IEC 60079-14-96).
It will be useful to read: