How are premises classified according to the degree of electrical hazard?
Main classification
According to the rules of the electrical installation (PUE) section 1.1.13, household and industrial, commercial, office premises are divided into classes:
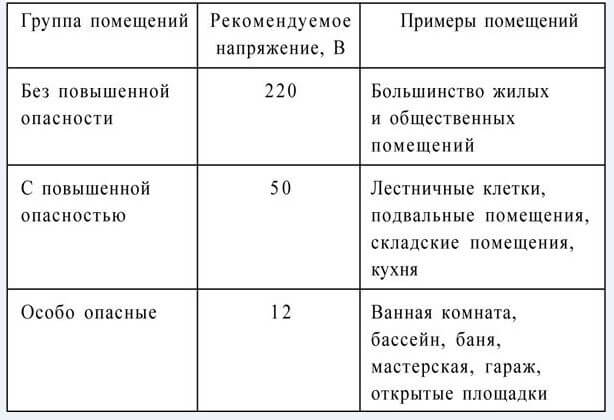
First grade - premises without increased danger. They are characterized by dryness (humidity does not exceed 45%), the possibility of adequate ventilation, the presence of a heating system (temperature should not be lower than 18-20 ° C) and the absence of dust. In addition, safe rooms must have dielectric floors and a fill factor of less than 0.2 with metal objects.
Second class - premises with increased danger, in which there are factors representing the danger of electric shock to a person.
In turn, the second class is divided into groups representing danger:
- high humidity (up to 100%);
- high air temperature (over 30 ° C);
- poor airing;
- dustiness
- conductive floors, walls.
- conditions under which there is the possibility of simultaneous contact of a person with grounded structures, walls, columns, floor and with the body of technological mechanisms, electrical equipment.
Third class - This is a particularly hazardous area (the presence of chemically active substances, high humidity, the presence of two or more dangerous conditions).
They also distinguish a group - the territory of open electrical installations, which is equated as especially dangerous.
The picture below shows how rooms are classified according to the danger of electric shock:
Special requirements and protective measures are imposed on the placement and operation of electrical equipment in such premises (for example, equipping workers with special uniforms, which increases the body's resistance).
What is the danger?
As we know, wet objects and water directly contribute to an increase in electrical conductivity, so any room with high humidity can be classified as dangerous (especially if moisture constantly accumulates on the floor, ceiling and walls).
Another category is dusty rooms. Dust can collect on electrical installations and contribute to the occurrence of conductive paths, which leads to overheating and fire of electrical equipment.
High air temperatures lead to aging of the insulation and lower insulation properties of the protective coatings, which can also lead to an emergency.
The metal floor is a danger, such as in the conditions of simultaneous contact with electrical equipment and the grounded part of the building.
Reactive substances can affect the insulation of electrical equipment, as well as contribute to the emergence of current paths from oxides.
It should be noted that in order to increase safety at work, various measures are used: fire protection of cable lines, installation of ventilation systems, laying of dielectric flooring. All this allows to minimize personal injuries that occur when working with electrical equipment!
The table below provides recommendations on the use of voltage values in various categories of premises:
So we examined the main classification of premises according to the danger of electric shock. We hope that the information provided was useful to you and now you know how the various rooms are divided according to the degree of electrical safety and what this indicator is characterized by!
Recommended reading: