What is a load cell and how does it work
Types and scope
To begin with, we will understand in principle the operation of strain gauge sensors. When an external force acts on a body, it deforms and counteracts the applied force. Due to deformation of the sensor housing, an effect is made on the measuring element of the strain gauge. As a result, the device generates an electrical signal, reading which the processing system gives the measurement result. But what is this type of device for?
Strain gages are used for:
- Weight measurements. Moreover, depending on the design of the measuring unit, they can be used for compression or tension. Accordingly, their purpose is to measure weight on platforms (for example, scales in stores) or on a suspension (cranes, etc.).
- Pressure measurements. For example, in pipelines of gases and liquid substances.
- Torque measurements (on car engines or machine tools).
- Acceleration Definitions.
- Movement control.
By the type of measuring element and the principle of operation, the load cells are divided into:
- Resistive.
- Piezoelectric.
- Optical polarization.
- Fiber optic.
- Piezoresistive.
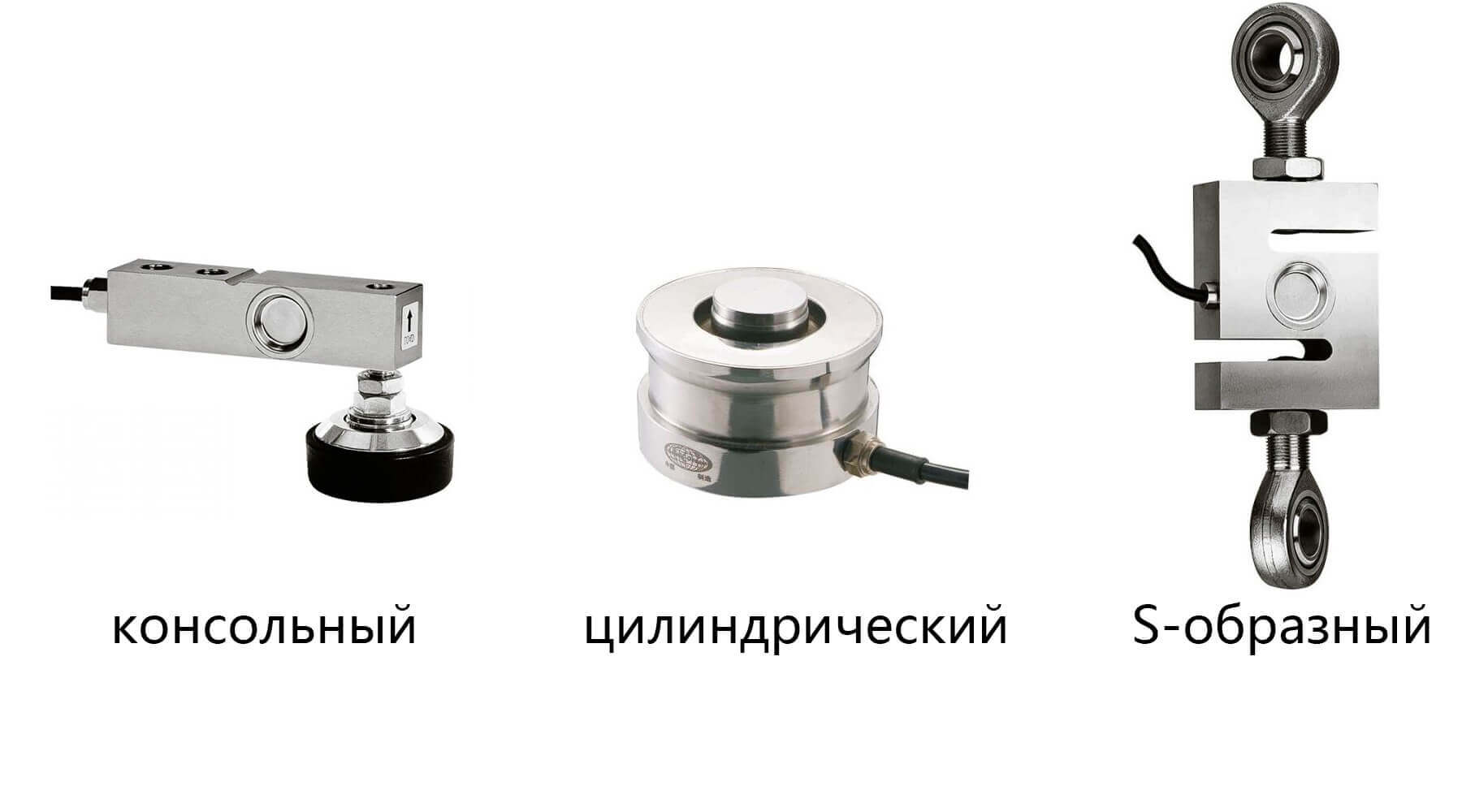
The design features of the load cell determines where it is used, because the design determines the presence of mounting holes and vectors of the possible application of forces, respectively, and the measurement process itself. There are also different types of strain gauges in shape:
- Cantilever. The purpose of such devices is to measure the amount of substances in dispensers, conveyor, platform, hopper and floor scales.
- Cylindrical. They are used for weighing wagons, cars, tanks and containers - where you need to measure large weights.
- S-shaped, tensile, suitable for measuring the weight lifted by a crane and other similar designs.
In practice, strain gauges can be produced in a completely diverse design.
The device and principle of operation
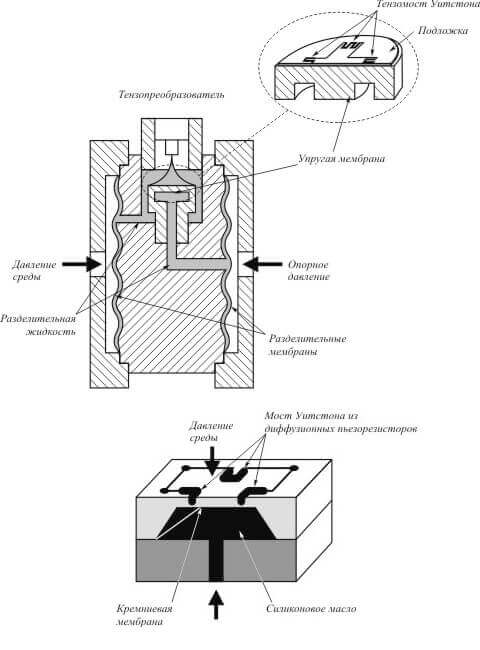
Strain gages are used to measure pressure or weight; all of them give an electric digital or analog electric signal when the shape of the sensitive element changes. But what are they made of?
The base or cases are of different types, it depends on where you can install the sensor. And also in what direction it works - for compression, tension or bending.
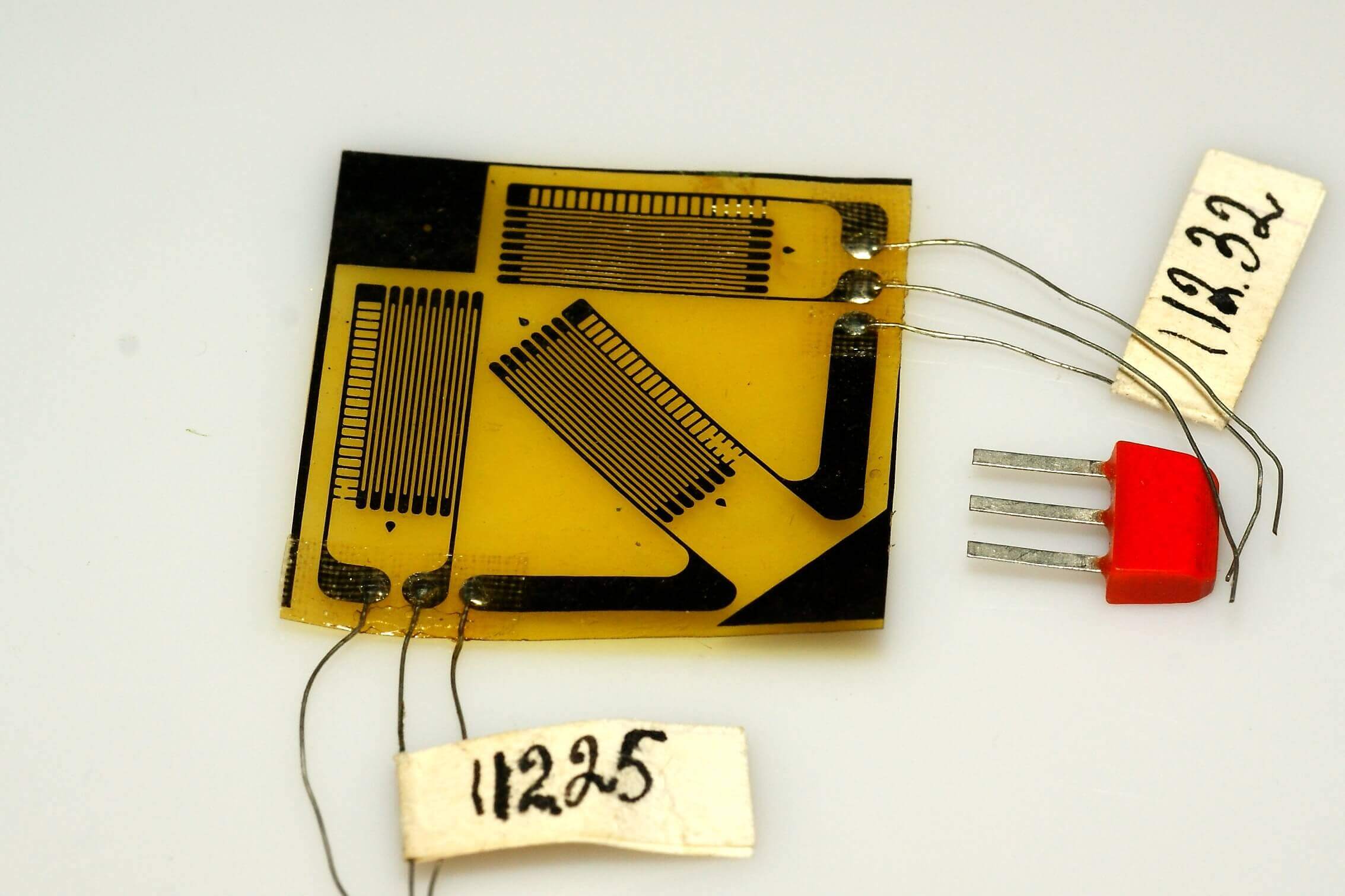
In addition to the sensing element, the load cell housing can also contain additional units, for example, an ADC, power drivers, etc. If the strain gauge is digital, then there is a unit for converting an analog signal (ADC).Consider the principle of operation of the sensor element of the strain gauge on the example of a strain-resisting component - they have found the most widespread application.
A resistive strain gauge is a flexible film or substrate on which a resistive layer is applied. If it is a film sensor - thin spraying or foil, if wire - on a flexible substrate wire is placed. Spraying or wire are laid in a winding line.
During mechanical action on the substrate, it bends, as a result of which the film, foil or wire is stretched. Accordingly, in a tense state, its cross-sectional area changes (decreases) and the resistance increases. When the pressure decreases, the substrate returns to its original position, the resistive layer also, and its resistance begins to decrease and returns to normal.
Piezoelectric sensitive organs work opposite. When pressure is applied to the piezocrystal, an EMF occurs, while the resistance of piezoresistive sensors made of thin films of semiconductors also changes.
You can also find capacitive sensors - these are devices whose principle of operation is to measure the capacitance between flexible plates. As well as electromagnetic devices in which, under the influence on the magnetic circuit, the characteristics of the circuit change.
Wiring diagram
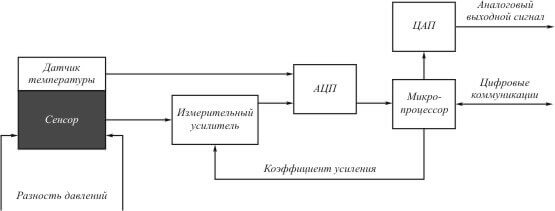
How the load cell works, we figured out. Now you should familiarize yourself with the connection diagram. The block diagram of the device that reads the signal is shown in the figure below. On it you see one of the options for amplifying and converting the signal from the sensor.
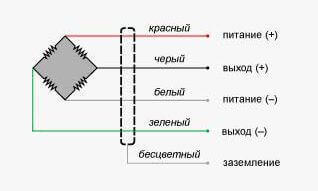
If we consider the strain gauge sensor, then in reality it is a bridge of resistors, included as follows. This switching circuit is called the "Winston Bridge" or the measuring bridge.
For its operation, it is not enough to connect only signal wires, you also need power wires. In some complex systems, wires can also be connected for thermal stabilization or other functions.
The video tells in detail what the strain gauge sensors are and how they work:
Modern strain gauge sensors, depending on their purpose, can be used in installations for measuring from fractions of a gram to hundreds of tons. Accordingly, for each range of weights, strain gauges of a certain design and type of sensitive element are selected. In addition to the measured weights, the conditions in which they will operate, as well as the required accuracy class, play an important role in the selection of instrumentation.
Related materials: