What are fuses and what are they for?
How does the device work?
The fuse operates in two modes that are significantly different from each other.
- Normal network mode. In this mode, the heating of the device occurs as a steady process. At the same time, it is completely heated to a certain temperature and gives off the released heat to the environment. On each element, the so-called rated current strength is indicated (as a rule, the highest current value of the structural element is indicated). A fuse of different rated currents can be inserted into the fuse.
- Short circuit mode and overloads. The device is designed so that with increasing current strength in the network, it could burn out in the shortest time. For this, the fusible element in individual sections is made with a smaller cross section, where more heat is released than in wide sections. At short circuit almost all or all of the narrowed areas burn out. When an element melts, an electric arc is created around it, the extinction of which occurs in the cartridge of the mechanism.
The current strength should be indicated on the device body, and the maximum permitted voltage at which the device does not fail should also be taken into account.
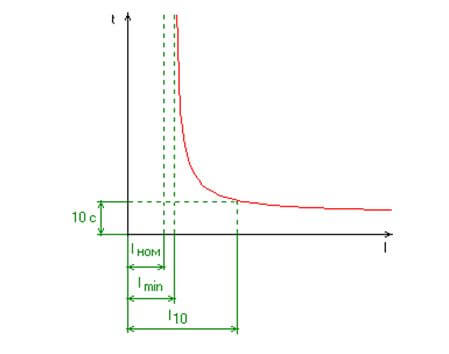
The graph below shows the dependence of the fuse burnout time on current:
Where l10 is the current at which the element melts and disconnects it from the network for 10 s.
Varieties and types of elements
Fuses are divided into two types: low voltage and high voltage. This division is explained by the magnitude of the voltage of the working mains in which the fuse is used.
Low-voltage devices are marked as MV or OL and are rated for voltages up to 1000 V. In low-voltage MV devices, a fine-grained filler is located around the copper insert. Their application is calculated up to 630 Amps.
The PR device is simpler (in the photo below) than the PN, but with a short circuit, and they are able to extinguish an electric arc. Designed for currents from 15 to 60 amperes.
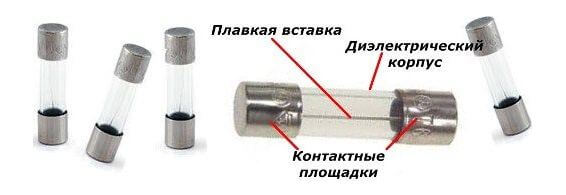
By design features, fuses are divided into cartridge, cork, plastic and tubular. By the type of execution produce collapsible and non-collapsible products. Collapsible have the ability to access the insert. The design is disassembled and the burned-in insert is replaced with a new one. Non-separable are constructed from a glass flask, therefore, they are considered disposable and cannot be replaced.
Design
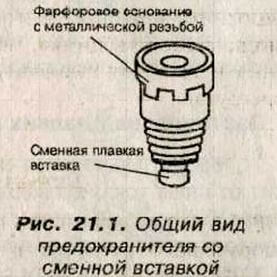
The modern fuse consists of two parts:
- a base of electrical insulation material with metal thread (necessary for connection to an electrical circuit);
- replaceable insert that melts.
The basis of the device is an insert that burns or melts during a short circuit. In order to extinguish the arc, which is formed as a result of burnout of the removable insert, extinguishing devices are installed.
The terminals of the insert are connected to the terminals so that the fuse is connected to the electrical circuit line. For this, special reliable fixing terminals (holders) are used, which should provide good contact. If it does not exist, then heating may occur in this place.
A feature of the design of fuses is that the device burns out before other parts of the mechanism are damaged. After all, it is easier to replace than a microcircuit or other component of the equipment. Therefore, such a part is chosen taking into account that its melting rate is greater than in the wires of the line. Their temperature should not reach a dangerous level, as this will lead to equipment failure.
The design of the mechanism of the plug type has the form of a cartridge into which a fuse with a cap is screwed. If an emergency occurs, the plug will burn out. Today, this cork looks like a button, similar to a conventional switch. This button after an accident returns the device to working condition.
In addition to the fact that the fusible component protects the electrical circuit from damage, it also protects against fires and fires. After all, a conventional wire may come into contact with combustible materials at the time of ignition, and the part burns inside the device.
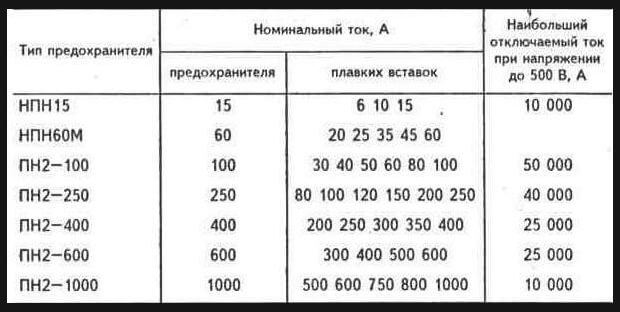
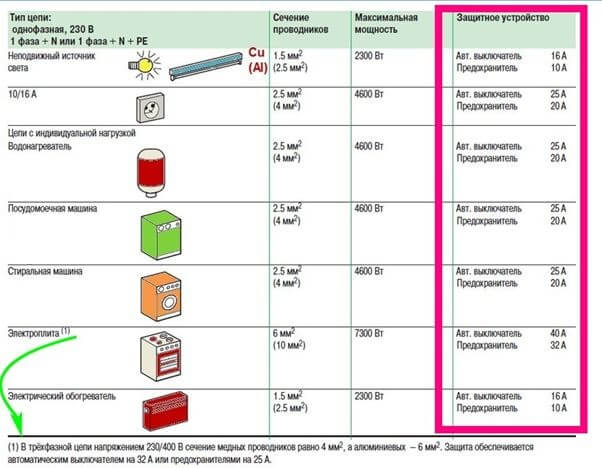
The device ratings are selected according to the lowest rated currents of the electric network or a separate part of the electric circuit. The rating table is provided below:
If it is necessary to change such a component to AB (circuit breakers), then their rating should be one step larger than the component part. For instance:
About, how to replace traffic jams with automatic machines with your own hands, we told in the corresponding article.
Finally, we recommend watching a useful video on the topic:
So we examined the device, the principle of operation and the appointment of fuses. We hope the information provided was useful and interesting for you!
Surely you do not know: