What is a diode bridge - a simple explanation
Definition
The diode bridge is a circuitry solution designed for rectification of alternating current. Another name is a half-wave rectifier. It is built from semiconductor rectifier diodes or their variety - Schottky diodes.
The bridge circuit implies the presence of several (for a single-phase circuit - four) semiconductor diodes to which the load is connected.
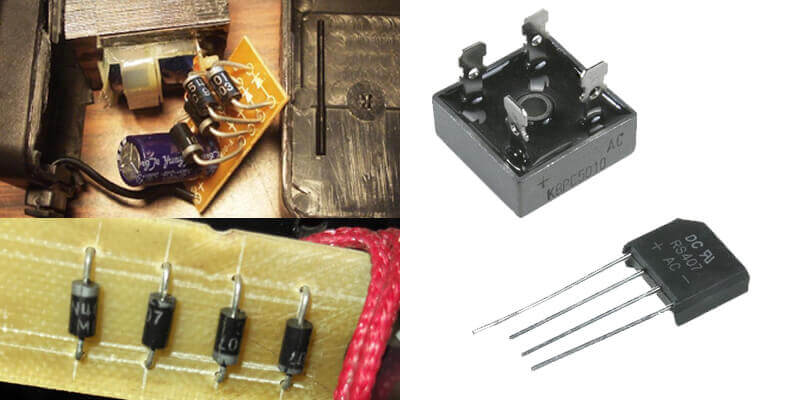
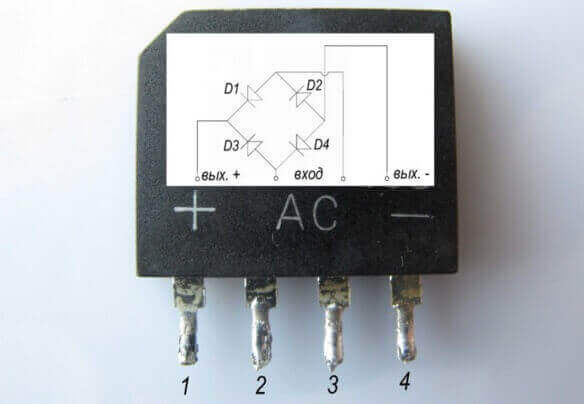
It may consist of discrete elements soldered on the board, but in the 21st century, more often connected diodes in a separate housing. Outwardly, it looks like any other electronic component - legs for connecting to the tracks of the printed circuit board are removed from the case of a certain size.
It is worth noting that several valves combined in one housing, which are not connected according to a bridge circuit, are called diode assemblies.
Depending on the scope and connection diagram, diode bridges are:
- single phase;
- three-phase.
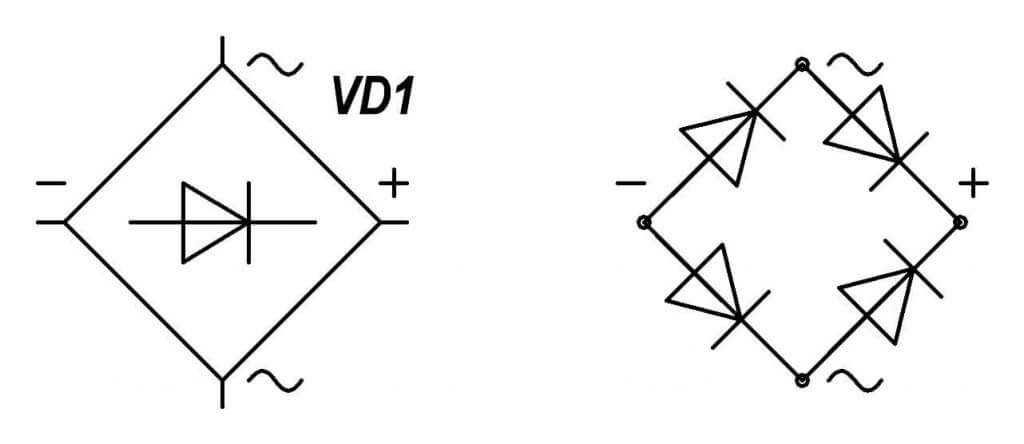
The designation on the diagram can be performed in two versions, which one to use UGO in the drawing depends on whether the bridge is assembled from separate elements or the finished one is used.
Operating principle
Let's understand how the diode bridge works. To begin with, diodes pass current in one direction. The rectification of the alternating voltage occurs due to the one-sided conductivity of the diodes. Due to their correct connection, the negative half-wave of the alternating voltage enters the load in the form of a positive. In simple words - it flips the negative half-wave.
For simplicity and clarity, we consider its operation as an example of a single-phase two-half-wave rectifier.
The principle of operation of the circuit is based on the fact that diodes conduct current in one direction and consists in the following:
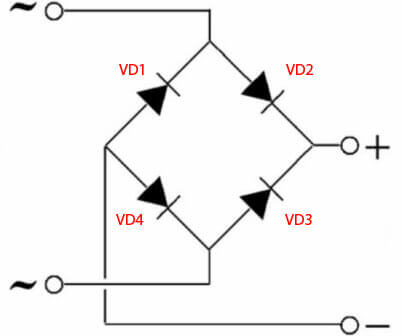
- An alternating sinusoidal signal is fed to the input of the diode bridge, for example 220V from the household power supply (in the wiring diagram, the diode bridge input is indicated as AC or ~).
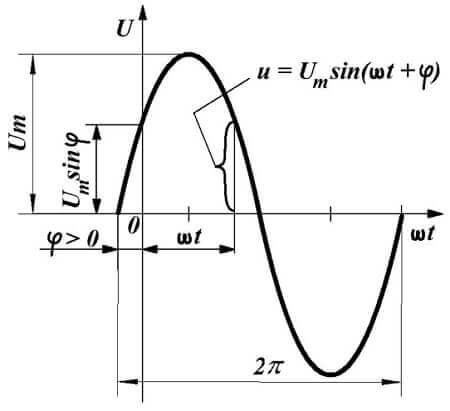
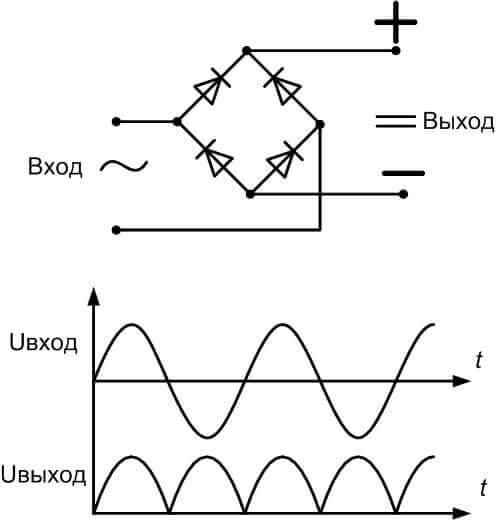
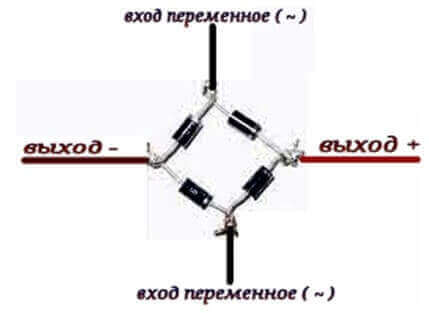
- Each of the half-waves of the sinusoidal voltage (figure below) is passed through a pair of valves located diagonally on the circuit.
The positive half-wave is passed through the diodes VD1, VD3, and the negative - VD2 and VD4. The signal at the input and output of the circuit you see below.
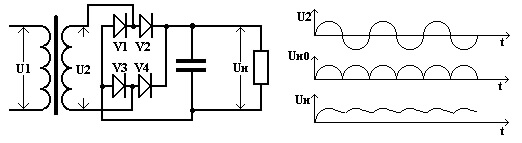
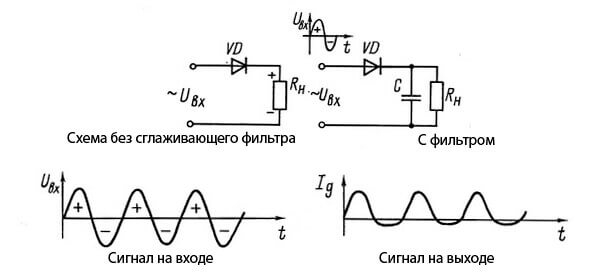
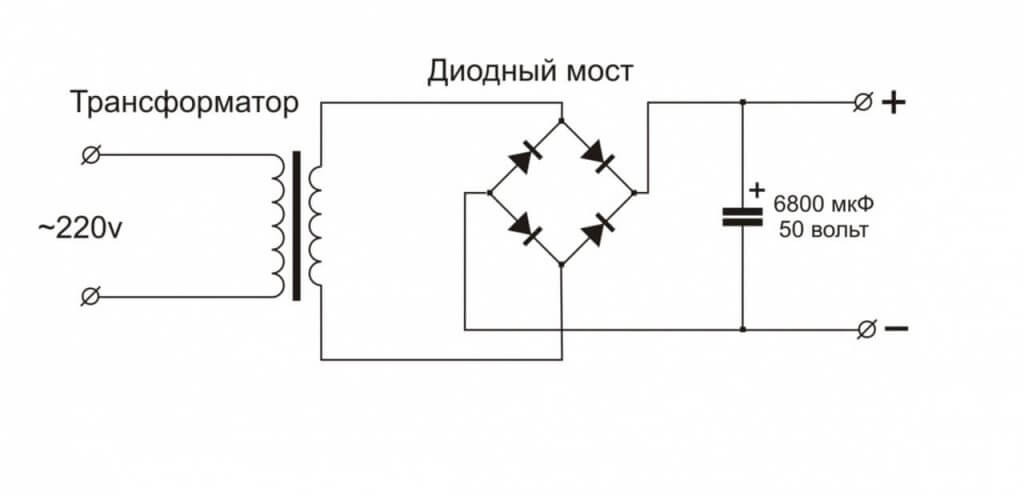
This signal is called - rectified ripple voltage. In order to smooth it, a filter with a capacitor is added to the circuit.
Main characteristics
Consider the main characteristics of semiconductor diodes. Latin letters indicate their designation in the English-language technical documentation (the so-called Datasheet):
- Vrpm - peak or maximum reverse voltage. When this voltage is exceeded, the pn junction is irreversibly destroyed.
- Vr (rms) - average reverse voltage. Normal for work, same as Uarr in the characteristics of domestic components.
- Io - average rectified current, the same as Ietc in domestic.
- Ifsm - peak rectified current.
- Vfm - voltage drop in forward bias (in the open conductive state) is usually 0.6-0.7V, and more with high-current models.
When repairing electronic equipment and power supplies or designing them, beginners ask: how to choose the diode bridge?
In this case, the most important parameters for you will be the reverse voltage and current. For example, to select a diode bridge for 220V, you need to look at models with a rated voltage of more than 400V and the desired current, for example, KBPC106 (or 108, 110). Its technical characteristics:
- maximum rectified current - 3A;
- peak current (short-term) - 50A;
- reverse voltage - 600V (800V, 1000V for KBPC108 and 110, respectively).
Remember these characteristics and you can easily determine which option to choose from the catalog.
Rectifier circuits
The rectification of the current in the power supplies is the main purpose, among the other components of the circuit, you can select the input filter, which is connected after the rectifier - it is designed to smooth ripple. Let's look into this issue in more detail!
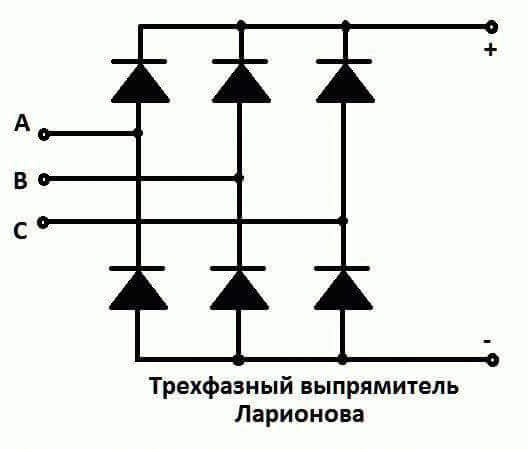
First of all, it is worth noting that a diode bridge is called a single-phase rectifier circuit of 4 diodes or a three-phase of 6. But fans often call the rectifier circuit with a midpoint.
In a half-wave rectifier, two half-waves arrive at the load, and in a half-wave rectifier, one.
To avoid confusion, let's understand the terminology.
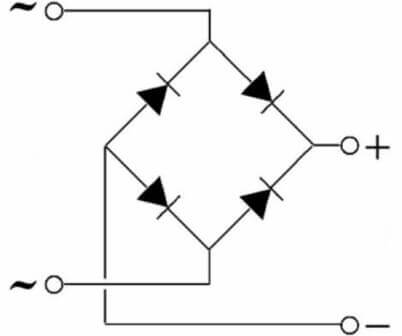
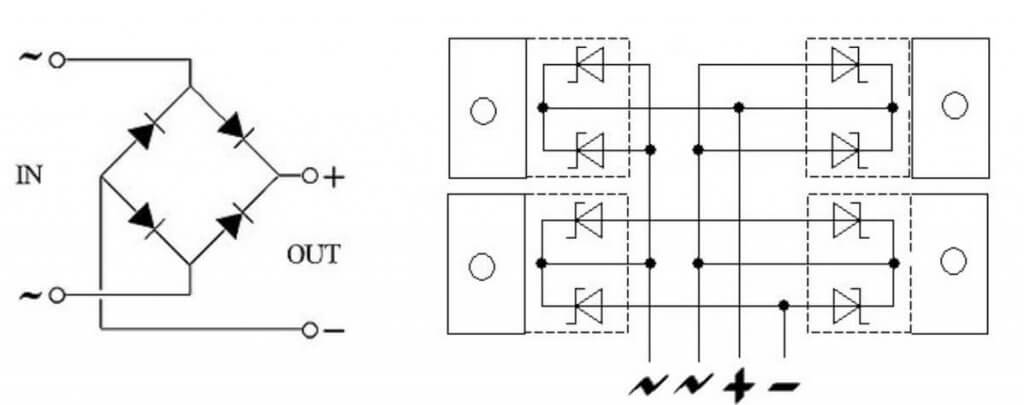
Below you see a single-phase two-half-wave circuit, its correct name is “Gretz circuit”, it is precisely its most often implied by the name “diode bridge”.
Larionov's circuit is a three-phase diode bridge, the output signal is half-wave. Diodes in it pass half-waves, opening on line voltage, i.e. alternately: an upper phase A diode and a lower phase B diode, an upper phase B and a lower phase C, etc.
For completeness, it is necessary to talk about other schemes of AC voltage rectifiers.
A half-wave rectifier of 1 diode connected in series with the load. It is used in ballast power supplies, low-power miniature power supplies, as well as in devices that are undemanding to the ripple factor. Only one half-wave arrives at the load.
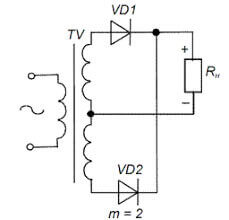
Half-wave with a midpoint - this is what is mistakenly called a bridge of 2 diodes. Here, only one diode conducts each half-wave. Its advantage is greater efficiency than the Gretz circuit, due to the smaller number of semiconductor gates. However, its use is complicated by the fact that you need a transformer with a tap from the midpoint, which is reflected in the circuit diagram. It cannot be used to rectify the mains voltage of 220V.
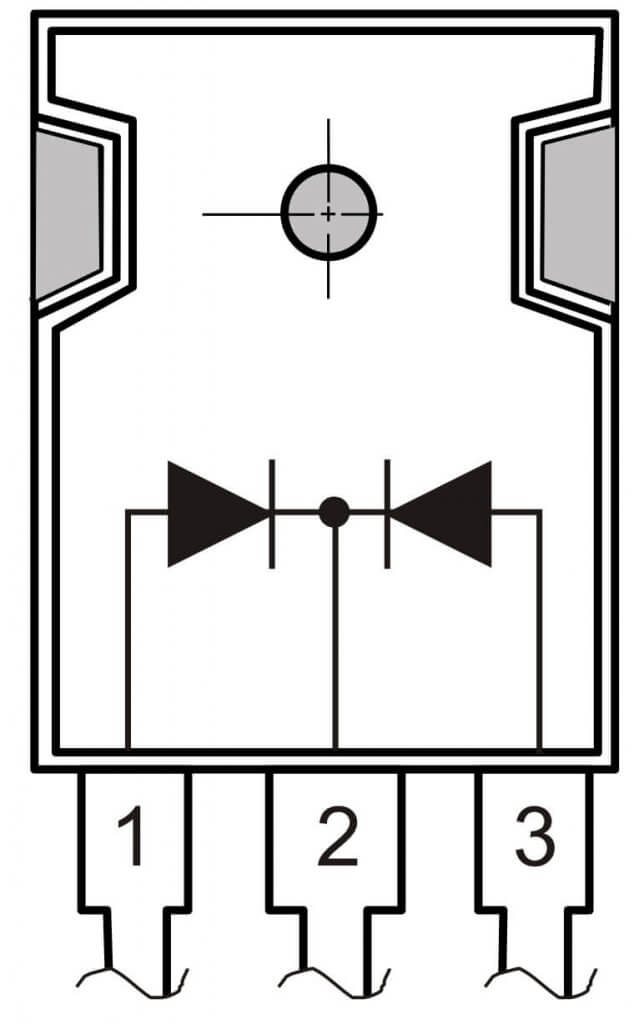
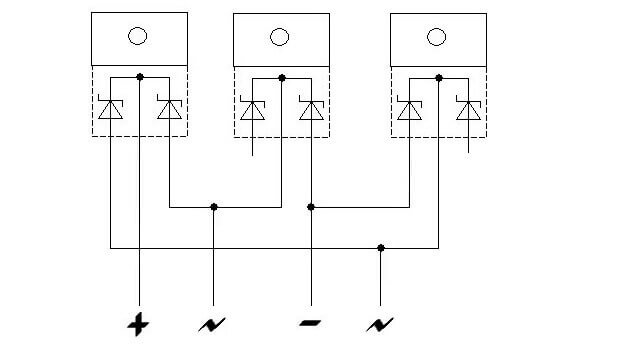
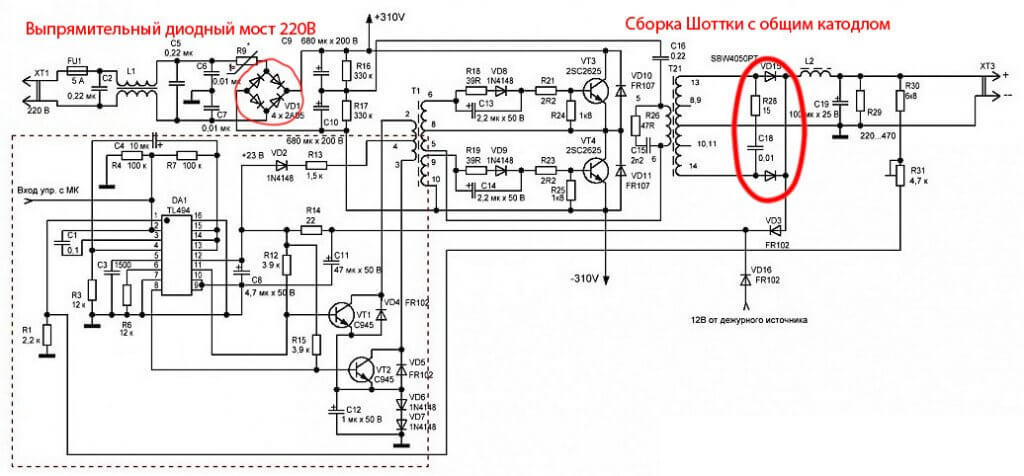
Rectifier from Schottky assemblies. It is used in switching power supplies, because Schottky diodes have less reverse recovery time, a small barrier capacitance (faster transition from open to closed state) and a small forward voltage drop (less losses). Schottky is most often found in assemblies with a common anode or cathode, as shown in the figure below.
Therefore, to assemble the bridge circuit, several assemblies will be required. Below is an example of 3 Schottky assemblies with a common cathode.
Of 4 assemblies with a common cathode. It differs from the previous one in that it can withstand more current, with the same components, because the Schottky wires in it are connected in parallel.
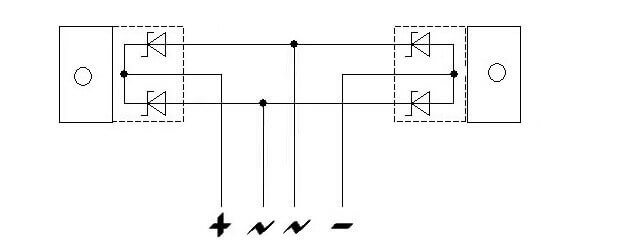
Of the 2 Schottky assemblies, one with a common anode and one with a common cathode. Learn about what is the anode and cathodeYou can in our separate article.
How to solder and connect
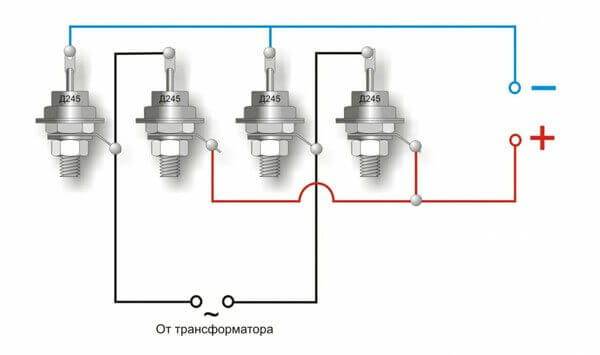
It is not difficult to study and know the circuits, the main difficulties arise when a beginner decides to solder a diode bridge with his own hands. To solder a rectifier from 4 Soviet copies of the type cd202, use the illustration below.
To assemble a diode bridge from modern discrete diodes such as low-power 1n4007 (and others - they all look similar and differ only in size) carefully look at the following illustration.
But if you do not assemble it from individual parts, but use a ready-made bridge, then see below how to properly connect it to the circuit.
It will also be interesting for beginners to watch a video on how to make a simple 12V power supply:
Scope and purpose
Most often, diode bridges are used in power supplies. In transformer power supplies, they are connected to the secondary winding of the transformer
In pulse power supplies - to the input of a 220V network. In this case, the electronic control circuit and the UPS power circuit is powered by a rectified and smoothed (not always) mains voltage (reaches about 300-310 Volts).
At the terminals of the secondary winding of the switching power supply, high-frequency alternating voltage. In order to straighten it, install assemblies of dual Schottky diodes. In this regard, a mid-point rectification scheme is often used.
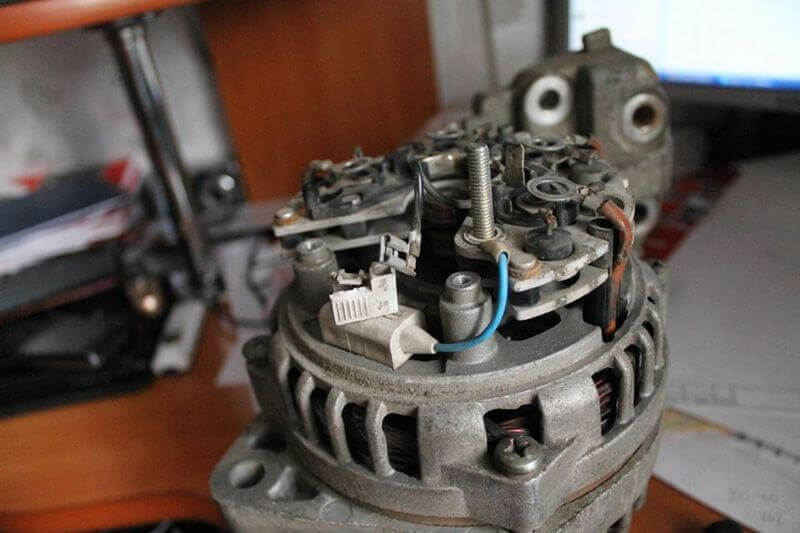
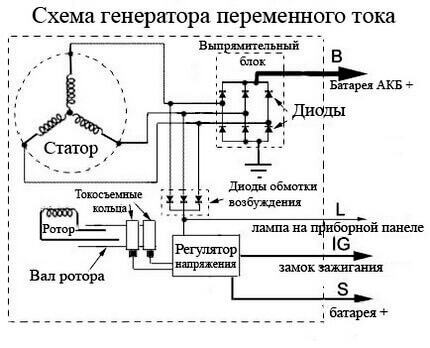
In cars and motorcycles, three-phase diode bridges are used, assembled according to the Larionov scheme with three additional valves, because a three-phase generator is used to power the on-board network. The bridge in the generator is made in the form of a sector of the circle and is installed on its rear.
An exception is some modern Toyota cars and other brands, they use a 6-phase generator to implement a twelve-pulse rectification circuit of 12 valves. This is necessary to reduce ripple and increase the output current.
Verification Methods
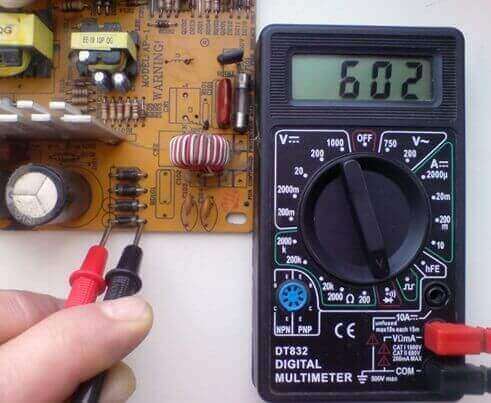
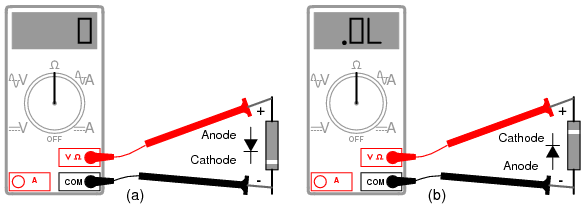
To test a diode bridge, a multimeter in diode test mode is best suited.
To do this, you need to ring the input, then the output for a short circuit (the diode bridge must be soldered).
Without soldering directly on the board, you can measure the voltage drop across the diode junctions. To do this, you need to determine the pinout of the bridge, usually it is indicated directly on the case, which we considered above.
On the screen of the multimeter, in the forward bias, the numbers should be displayed within the range of 500-800 mV, and in the reverse, above 1500 and to infinity (depends on the specific component and the measuring device). The same can be done in Ohmmeter mode, as shown in the figure below.
This process is described in more detail in the article “how to check the diode bridge”, Where in addition to the test methodology, we talked about the signs of a malfunction. Also check out the video on how to test a single-phase rectifier and diode bridge of a car generator:
That is where we end our detailed explanation. We hope that now it has become clear to you why a diode bridge is needed and what it does in an electrical circuit. If you have questions, ask them in the comments under the article!
Related materials: