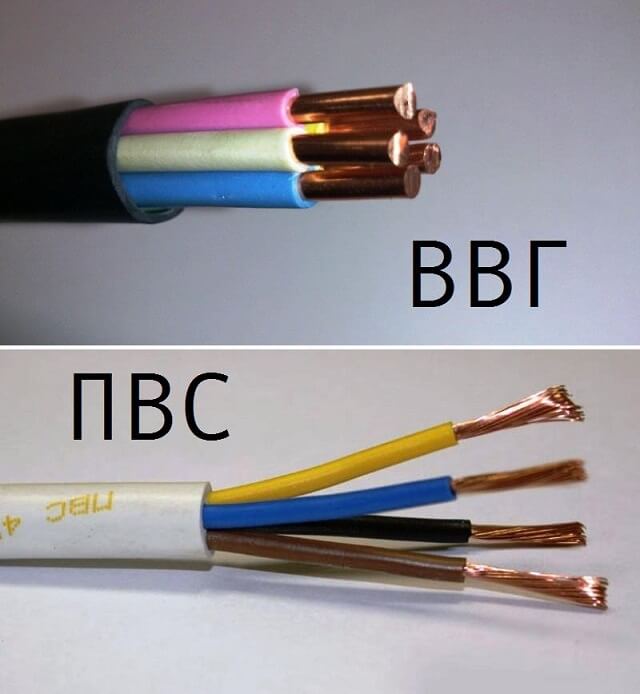
Which is better to choose: VVG cable or PVA wire?
Comparison of technical characteristics
For the convenience of comparing the main technical parameters of the conductors and understanding what the difference is between them, we will make a table comparing the main characteristics.
| Feature / Material | PVA wire | VVG cable |
| Core material and construction | Copper stranded | Copper stranded or solid |
| Flexibility | 5th class of flexibility (high) | 1 - 2 class of flexibility (average) |
| Number of cores in a wire / cable | 2 to 5 | 1 to 5 |
| Cross sectional area, mm2 | 0.75 to 6 | 1.5 to 625 |
| Permissible operating voltage, V | ||
| In alternating current circuits, at a frequency of 50 Hz | 450 volt | 0.66 kV or 1 kV |
| In DC circuits | 0.66 kV | 1.6 kV or 2.4 kV |
| Permissible ambient temperature | From -25 ° С to + 40 ° С | From -50 ° С to + 50 ° С |
| Permissible continuous core heating temperature | 70 ° C | 70 ° C in emergency operation, short-term heating up to 80 ° C is allowed |
| Regulatory life | From 6 years (mobile connection) to 10 years (fixed connection) | Up to 30 years. The manufacturer's operational warranty is 5 years. |
To understand what is best to apply in a given situation, you need to conduct a comparative analysis of individual properties that are decisive.
Conductor Properties. The cores of both conductor products in question are made of copper. PVA wire only available in the multi-wire version of the core, VVG cable may have an integral mono-wire core. The significant difference between the two lies in the flexibility class of the multiwire versions. In this parameter, PVA is many times superior to VVG. Due to this characteristic, the fatigue strength of a wire with repeated bends is significantly higher than that of a cable. That is, when it comes to mobile connections, the choice should be made in favor of PVA. Such connections include the supply of non-stationary electrical appliances, as well as electrical wiring with a plug for connecting electrical equipment to the network.
Core section. The table shows that the range of sections of VVG is much wider towards large values. In relation to the choice electrical wiring for home, apartments or cottages, we can say that the wiring of power circuits supplying power for the oven, for the hob or air conditioner, can only be done using a cable product of the appropriate section. The largest PVA cross section is 2.5mm2that is not enough for these purposes.
Insulation Properties and Total Life. Comparing the operating voltage at which the conductors in question can work, we determine the difference between one material and another. The fact that the permissible voltage for the cable is higher than for the wire indicates that when working in the same voltage class, the margin of electrical insulation of the cable is higher than that of the wire insulation. If we add the fact that the life of the VVG exceeds the similar indicator of PVA by at least three times, we can draw the following conclusion:
Installation of stationary electrical wiring, especially hidden, is more expedient to carry out using a VVG cable. In this case, it is better to use a monowire version of the core. Given that hidden wiring stacked for a very long time, its reliability should be as possible. It is better to use a cable version VVGng non-combustible insulation.
Environmental conditions. The range of permissible ambient temperatures for VVG is significantly expanded to the zone of negative temperatures in comparison with PVA. This fact is determined by the fact that a cable product more suitable for this should be chosen for the street.
To summarize
It can be summarized as follows. Each of the considered materials has application features. When choosing conductors for specific purposes, you should carefully understand what is the difference between VVG and PVA. In conclusion, I would like to list a couple of aspects that may affect the choice.
The first aspect is the price. It is possible that when a lower price determines the choice in favor of a particular material. In this case, you must accurately weigh all the disadvantages that are acquired with a gain in price.
The second aspect is design features. The cable can be flat, which in some cases creates additional convenience during installation. The wire, in turn, being softer, more conveniently fits into cable channels.
Finally, we recommend that you watch the video, which presents the opinion of experts:
We hope that the information provided helped you understand what is best to choose for electrical wiring: PVA or VVG and what is the difference between the two brands of conductive products under consideration!
Surely you do not know:






Since when did a multicore cable become a wire? Comrades "professionals", study at least the terminology, and then write articles! A wire is a single-core conductor with or without light insulation, and a cable, if simple, is several wires connected together, each with its own insulation and all together in common insulation. So do not mislead people. What you compared in the article is not a wire and cable, but two types of cable!
This is which side to look at. In terms of design, yes, these two conductors are considered cables. But the letter marking indicates that the PVA is a wire, therefore, the article also states as the manufacturer believes. Yes, in other matters, this article is not so important, here another foundation is laid!
PVA cross section from 0.75 to 2.5? Recently I bought 4x6 PVA ...
Since when did the PVA cable become the maximum cross-section of 2.5 mm2?
I have a 5x16mm cable in my warehouse for example.