What is the difference between the driver from the power supply and transformer
Most consumers of electric energy use 220 V AC, but many modern lighting devices require special power sources that provide reduced AC or DC voltage, or a stable current. To create the necessary operating conditions for low-voltage consumers are: an electronic transformer, power supply, driver. It is important to determine which device to choose in a particular situation, because it depends on how well and for how long the equipment will serve. Consider the properties of each converter separately and how the driver differs from the power supply and transformer.
Electronic transformer
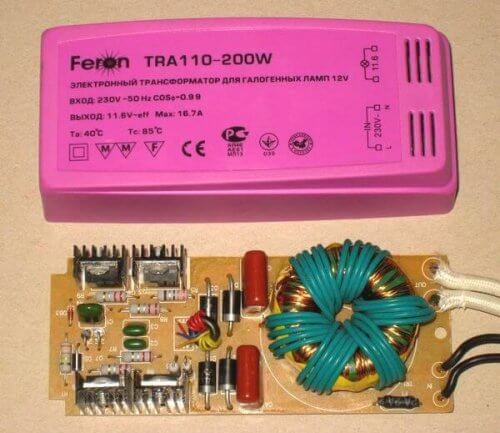
The simplest power source is a transformer. Its functions include increase or line voltage reduction.
Both an electronic and a conventional transformer have alternating current at the output, but what is the difference between them? The fact that electronic ones work at a high frequency, significantly exceeding the network 50 Hz, namely tens of kilohertz. This made it possible to reduce their weight and dimensions.
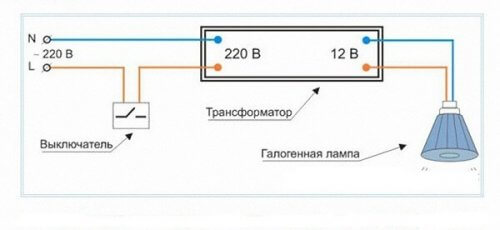
Electronic transformers are used to power halogen lamps at 12 V or 24 V.
If you connect such bulbs directly to the electrical network, they will burn out. But, if the halogen lamp is designed for 220 V, then a step-down transformer is not needed. The device is connected directly to the network.
This type of converter is not suitable for LED lamps and lamps. But the simplicity and cheapness of the device allowed its wide use for connecting halogen lamps.
When choosing a device, you must consider:
- output voltage (must correspond to the rated value of the connected device);
- rated power (if several halogen lamps are connected in parallel to the power supply, the power of each is summed up).
Such an electronic converter is placed in close proximity to the supplied light bulbs so that it does not overheat and provides natural ventilation. When mounting a local backlight, it is allowed to be mounted behind suspended ceilings, partitions, in cabinets. It is forbidden to turn on the transformer without load, and most models will simply not start at the same time.
DC power supply
A DC power supply unit is a device for lowering an alternating voltage from the mains to the required value, and converting it into a constant one.
Such PSUs are used for LED strips and for 12V LED lamps. It will be a mistake to use a transformer to power them, as this can reduce the service life, and also lead to a flicker of the light flux.
As you know, for the operation of LEDs need a stable current. But such power supplies only stabilize voltage. For this, in the LED strip, for example, current-limiting resistors are used. But such a solution is effective only for low-power diodes.
Driver
To connect high-power LEDs used in spotlights, in searchlights, street lamps, use the driver.
This device is a constant stabilized current source. When a load is connected to it, the voltage can change, but the current strength will have a clearly defined value.
Why is the driver used instead of the power supply to connect the LEDs?
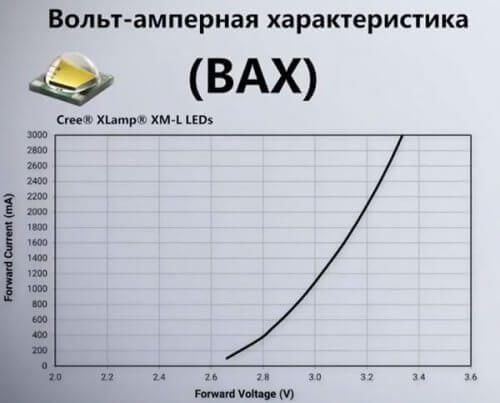
One of the characteristics of LEDs is voltage drop. If the characteristics of the semiconductor device have a record of 300 milliamps and 3.3 volts, this means that the rated current for the device is 300 mA, and the voltage drop is 3.3 V. And if you feed it with a stabilized current of this magnitude, it will last a long time and shine brightly.
From the graph of the current-voltage characteristic it is seen that even a slight increase in voltage will lead to a noticeable increase in current. And this is not a directly proportional dependence, but close to quadratic.
One could assume that by setting the exact voltage once, it will be possible to permanently set the value of the nominal current required for the operation of the LED light source. But each instance has unique parameters and properties, and when several pieces are connected in parallel or in series, the result will be unpredictable.
In addition, they are influenced by ambient temperature. The fact is that LEDs have a negative temperature coefficient of voltage (TKN). This means that during heating, the drop on the LED decreases, and the current rises if a stabilized, unchanging voltage is applied. For drivers, the output voltage varies depending on the load and its condition, and current is stabilized.
Therefore, if you use a regular power supply with a 12V constant when connecting the LED, the lamp will work, but the period will be reduced. To choose the right driver, you need to take into account its main technical characteristics:
- rated output current;
- maximum power;
- minimum power.
Sometimes the parameters for the device are indicated in a different form. For example, driver specifications 18-34V 650 mA (20 W):
- input voltage 85-277 V,
- output voltage 18-34 V,
- output current 650 mA.
That is, it is suitable for an LED matrix with characteristics: power - 20 W, voltage - 18-34 V, operating current - 650-700 mA or for 6-10 LEDs with a power of 2 W.
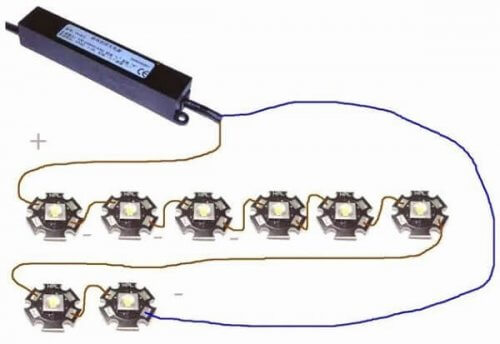
LED lights are connected to the driver in series, since in this case the same current will flow through all the elements. If they are connected in parallel, it may turn out that one of the elements will be overloaded, while the other will not work at full capacity.
In order not to exceed the maximum permissible load of the converter, it is not recommended to increase the number of LEDs in the circuit.
The driver is selected according to the current consumed by the LEDs. For example, a diode with a power of 1 W needs 300 - 350 mA.
This type of power supply has such disadvantages as:
- narrow specialization on LEDs;
- the ability to use only for a certain number of LED sources.
That is, for each device, a certain number of LEDs are selected. If in the process, one of them fails, the circuit will break and the driver will go into defense (or burn out), since the latter do not work in idle mode.
In conclusion, we note that despite the fact that the driver, power supply and electronic transformer are used to connect low-voltage consumers, these are completely different devices that differ from each other in purpose. It is important to understand in which cases each of them applies. After all, only a correctly selected power source can create optimal operating conditions for your equipment.
Related materials: