Decoding of marking wires and cables
Destination
The purpose of the cipher is to display the main characteristics, namely:
- the material lived;
- appointment;
- type of insulation;
- design feature;
- cross section of the product;
- Rated voltage.
If you are interested in information about how to mark wires during installation, we recommend that you read the article.
Main variety
To date, cords are used for electrical work, cables and wires. Before decoding the markings, it is necessary to understand what these products are and what are their differences.
Wires
A wire is an electrical product, consisting of one or more wires twisted together, without insulation or insulated. The core sheath is usually lightweight, not made of metal (although wire wrapping is also found).
- Bare conductor
- Insulated wire
Such products can be used in electrical work (for example, installation of electrical wiring in a wooden house), as well as in the manufacture of the motor winding. Today, there are wires with copper and aluminum conductors. The copper version is rapidly oxidized in open space and has a high price, but it is able to pass through higher current loads. In addition, copper is more elastic, which means it will not break so quickly. Aluminum is more fragile and does not connect with copper (except perhaps through the terminals), but for that they have a low cost. To date aluminum wiring used less and less.
It should also be noted that the contacts can be insulated and bare. The latter option is used for power lines. Insulated wire can be protected and unprotected. Protection is another layer of insulation (made of plastic or rubber), which covers the casing of the cores.
The last classification is carried out depending on the purpose: mounting, power and installation. The mounting wire must be copper, it is used, as a rule, to connect the elements of the electrical circuit in the switchboard, as well as to connect the circuit in the radio equipment. Power (as well as installation) for us is more famous, because used outdoors and indoors.
Cables
An electric cable is a product of several wires that are under one insulating sheath (made of PVC, rubber, plastic).In addition to this shell, additional protection may be present - an armored shell made of wire or steel tape, which must be indicated in the marking.
- Aluminum wire
- Copper contacts
There are 5 main types of electrical cables:
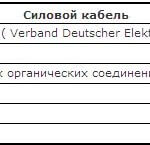
- power;
- control;
- For driving;
- for communication;
- radio frequency.
Briefly consider the conditions of use of each of the products.
Power It is used to transmit electricity in power and lighting electrical appliances. There are products of various types and purposes. Power cables are mainly used for electrical wiring external (both by air and underground) and internal (in residential and non-residential premises). Power cables can have both aluminum and copper conductors. Preference is given to the latter option. The insulating layer may be PVC, paper, rubber, polyethylene, etc.
Control It is used to operate electrical devices that transmit an information signal to control any devices. This type can also be with aluminum and copper cores.
Cable management It is a copper conductor with a protective shield. It is used in various automation systems. The protective screen serves to reject interference, as well as protection against mechanical damage.
Cable communication used to transmit information using currents of various frequencies. Local communication lines are transmitted by low-frequency conductors, and distant lines by high-frequency ones.
Radio frequency cable is used in radio devices. The main purpose is the transmission of video and radio signals.
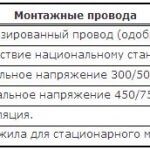
Cords
The cord consists of several (at least two) elastic cores of a small cross-section (up to 1.5 mm2). The cores of the cord consist of many interwoven wires, the insulation of which is carried out by a non-metallic sheath. Typically, the cords are multicore products, but there are two-core ones that are used if the appliance body does not require special grounding. Today, cords are used for connecting household appliances to the network (for example, a refrigerator or a microwave).
So we figured out the main differences between all three types of electrical products. We hope that the information was available to you. We also recommend watching a video in which this information is presented more clearly:
General differences
All conductors may have differences in the following ways:
- Transverse section. There are veins with a cross section of 0.35 mm2. up to 240 mm sq.
- Production material: copper, aluminum, aluminum-copper (a special composite of two metals).
- Rated voltage (for example, it can withstand 220 or 380V).
- Number of cores (single or multi-core).
- Insulation material (PVC, rubber, paper).
- Material of the containment (rubber, plastics, metal).
Marking
general information
The basic standards for marking wires, cables and cords according to GOST are the same, so first we consider the decoding of the letter cipher in an electrician.
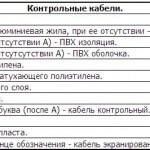
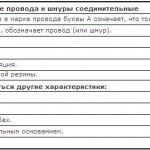
Letter No. 1 characterizes the core material. The letter “A” is assigned to aluminum; the letter is not assigned to copper.
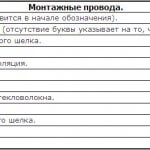
The letter No. 2 in the marking characterizes the type of wire or the material of the cable sheath. For the wire, the second letter means “P” - flat, “M” - mounting, “K” - control, “MG” - mounting with a flexible core, “P (U) or W” - installation.
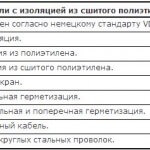
Letter No. 3 characterizes the material for insulation of cores. The letter “B” or “BP” means that the insulation is polyvinyl chloride, “P” is rubber, “N” or “HP” is nayritic (rubber that does not burn), “P” is polyethylene, “K” is kapron, “F "- metal (folded)," ME "- enamelled," L "- varnished," W "- polyamide silk," O "- polyamide silk as a braid," C "fiberglass," E "- shielded insulation," T "- insulation with a supporting cable," G "- insulation with flexible core.
In addition, it should be noted that the wire with rubber insulation can be additionally protected by the following type of sheath: “N” - nairitic, “B” - PVC.We draw your attention to the fact that these letters are put in the marking after the insulation material of the core itself is indicated.
Letter No. 4 characterizes the design feature. If the letter “A” is written, then the product is asphalted, “B” - armored tapes, “G” - without a protective cover (if the cable) and flexible (if the wire), “K” - armored with round wires, “T” is intended for laying in pipes, “O” - protected by a braid.
Decoding of the digital designation:
The number 1 always indicates the number of cores, if there is no number in front of the letters in the marking of the wire or cable, then the conductor is single-core.
The number 2 characterizes the cross-sectional area in mm.kv.
The number 3 displays the rated mains voltage.
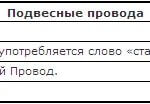
Marking of the cords is represented by the letter "W".
To readersour.electricianexp"Understood the whole point, we provide this example:
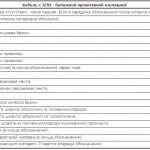
Explanation of the marking of the cable VVG 4 * 2.5-380. So:
- there are no letters "P" and "A", so there lived a copper;
- the second letter "B" indicates that the insulation is polyvinyl chloride;
- the second letter “B” is also indicated, which means another protection with a PVC sheath;
- the last letter - "G" means that there is no protective cover;
- the first digit is “4” - four cores;
- "2.5" - cross section in mm.kv .;
- 380 - Rated voltage of 380 V.
We hope that now you understand the labeling. If you have any questions, immediately ask them in the category "Question answer»!
Russian products
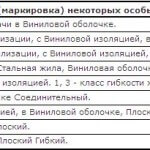
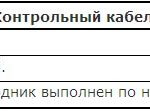
Marking of Russian cables:
Designation of domestic wires and cords:
Foreign products
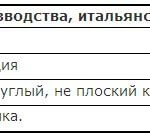
Marking tables of foreign cables:
Marking tables of foreign wires:
Tables
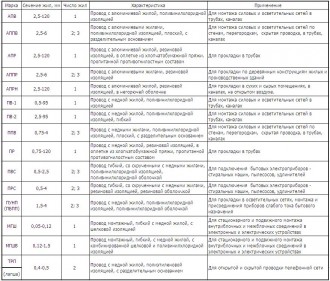
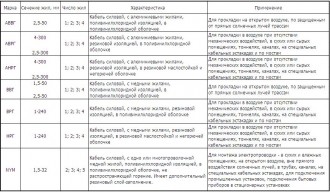
Brands and purpose of popular wires:
Brands and applications of popular cables:
Brands and destination of popular cords:
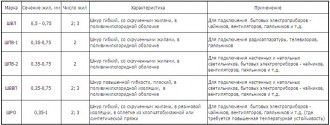 Using these tables and information, you can easily determine the characteristics and purpose of any conductor when installing electrical wiring in your own house or apartment. We hope that the provided marking of wires and cables according to GOST was useful to you!
Using these tables and information, you can easily determine the characteristics and purpose of any conductor when installing electrical wiring in your own house or apartment. We hope that the provided marking of wires and cables according to GOST was useful to you!
Also read: