Why are contacts heated and what can this lead to
Causes of Bad Contact
Poor contact can occur due to poor connection of the terminals or twisting (by the way, they are prohibited by the PUE), with the direct connection of aluminum with copper, from the influence of the environment. All these factors equally affect the quality of the contact and its heating. The problem is increasing transition resistance between live parts, i.e. wires or tires.
If the contacts are tightened poorly, the resistance increases. As a result of increasing resistance, according to Joule-Lenz Law the amount of heat generated also increases. As a result, the metal expands. The contact density is violated, and after cooling the junction, the resistance becomes even greater. As a result of the expansion of the conductors after they have cooled to their initial state, the terminal clamp or twisting density weakens.
According to the PUE, the contact resistance norm is the maximum allowable value of 0.05 Ohm. It is checked using a milliometer with a high accuracy class (at least 0.01 Ohm error).
The second reason is the weakening of the twist from vibrations. From mechanical stress, the connection of conductors may weaken. Contact becomes worse, resistance is greater, as a result, we have heating of contact compounds, which contributes to the deterioration of the situation.
The third reason is humidity. Conductors are oxidized from this, and the consequences are the same as in previous cases.
The fourth reason is the irresponsibility of wiring. Twisting of aluminum with copper should not be allowed - these metals are far from each other in a series of tension. From a chemistry course it is known that in this case corrosion occurs as a result of electrolysis, and it only contributes to an increase in resistance and heating.
As already mentioned: twisting as such are prohibited, and the direct contact of aluminum with copper even more so. In the case of a bolted connection between wires of different metals, a washer must be laid. Better yet, use terminal blocks, such as the now popular ones. Wago, for a domestic load they are enough, but for the installation of lighting - they are ideal.
The higher the resistance, the more heat is released, this leads to the fact that the compounds not only oxidize, but also cause a burning layer to form on their surface, which further exacerbates the situation.In the best case, the current simply stops flowing through this connection, you get an open circuit.
Examples from practice: sockets, automatic machines, knife switches
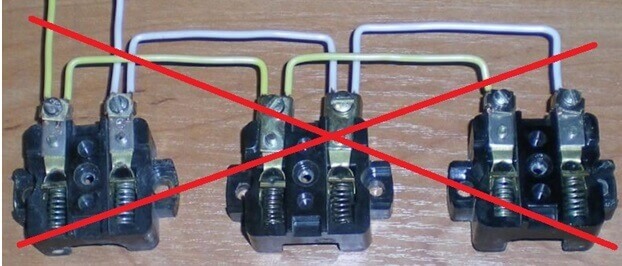
The first case is outlets: problems with outlets are a common cause of fires in apartments. The heating of the contacts in the socket can occur due to poor pulling of wires during installation or loosening of the screw clamp from time to time. This happens especially often when installing outlets with a loop, then the first outlet in the circuit is especially hot.
In such a circuit, in each of the outlets you need to connect two pairs of wires, one incoming and one outgoing. This method of connection, of course, saves the amount of cable during installation, but it can significantly complicate life in the future, because the whole load lies on one line.
In addition, if wires of different sections are connected in one clamp, the pressure plate is skewed, and this reduces the reliability of electrical devices. A wire with a large cross-section will be clamped tightly, but with a smaller cross-section it will loosely, or will generally jump out over time. As a result, increased heating of the contact compounds can be obtained.
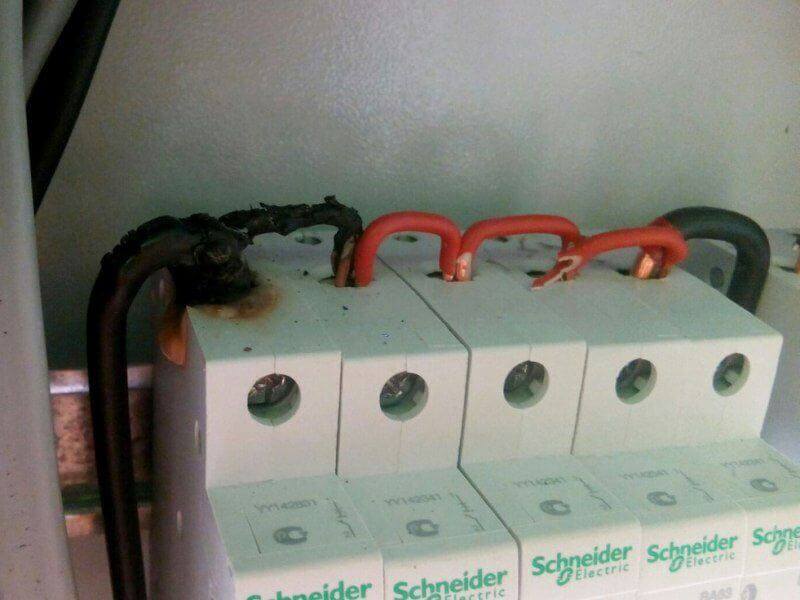
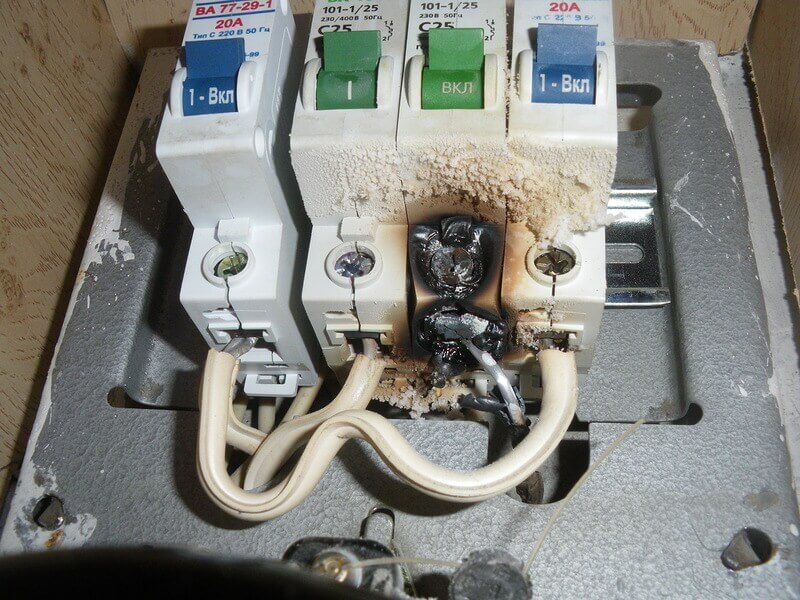
The second case is circuit breakers. Particularly relevant is the problem on machines installed on a din rail, which are powered from a single input through jumpers. In general, the terminals of circuit breakers are flat and rounded, it also depends on how the connections heat up. The contact area is greater, the more the terminal follows the shape of the conductor. As a result, sooner or later you will get this picture:
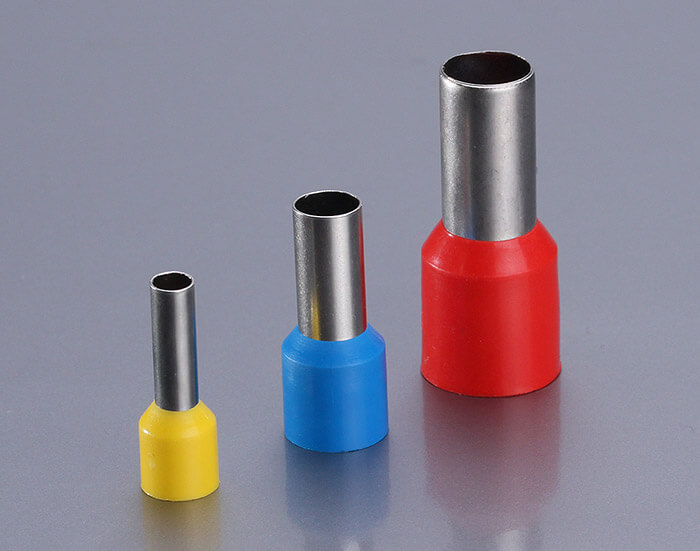
Important! If the cable cores are multi-wire, you must first wear tips or tin them with solder. Otherwise, the clamp of the circuit breaker (and any other terminal) will flatten the wire, such a connection heats up and is not very reliable.
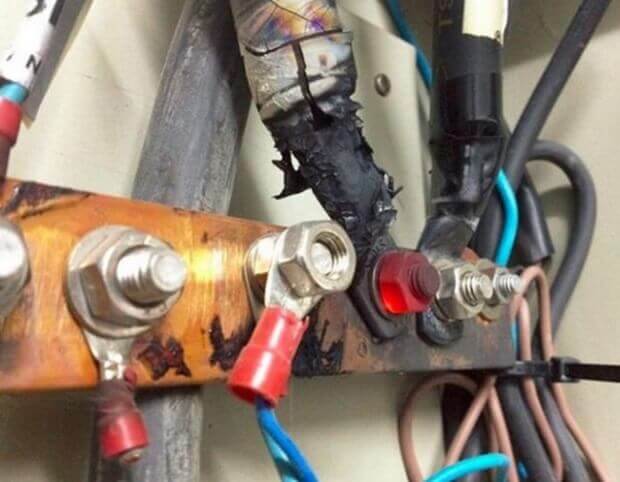
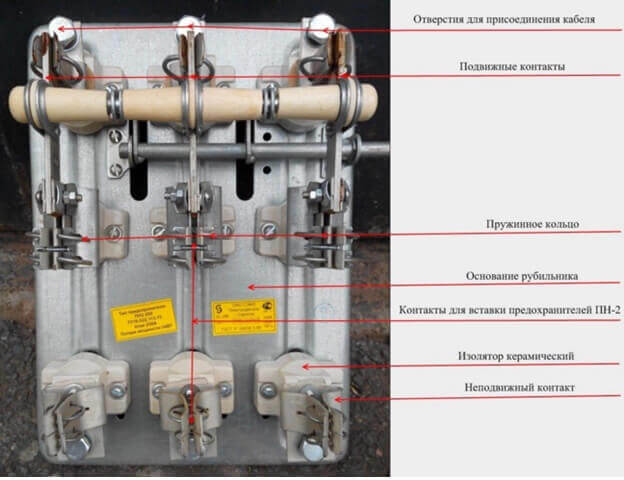
Another case is a knife switch. Often, in breakers and welding posts, bolted connections and fuse groups are used. Their use is typical for construction and production, where you often need to connect and disconnect equipment. In large electrical cabinets, a circuit breaker is also installed, and consumers are connected to the buses through fuses.
The bolt clamps are visible at the bottom. The consumer is connected to them, it is important to use cable lugs of this type:
The second problem is the weakening and heating of the contact of the knives, here you need to check their complete entry into the mating part and crimp if it is broken.
How to measure contact heating temperature
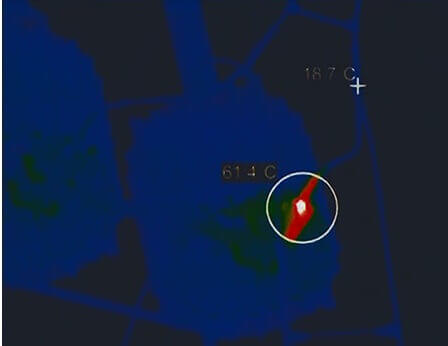
The safest way is to use non-contact pyrometers or thermal imagers. They pick up infrared radiation. Heat is infrared radiation.
A special thermal imager matrix detects radiation in the infrared range and displays a visual image on the screen. Both methods allow you to determine the heating without turning off the voltage, which is extremely important when examining and diagnosing high-voltage lines. The photo shows how the network elements heat up:
The main condition for reliable contact is the absence of carbon deposits and oxides, compliance with installation rules, the use of ferrules and tight crimping of the contacts. Otherwise, contact heating and loss will occur. Follow all of these tips and you will avoid problems in the future.
It will be useful to read: