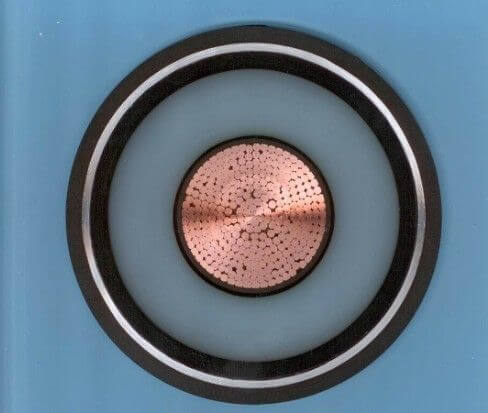
Design features of wires and cables
Structural elements
Any electrical conductor consists of the following parts, not always from all at once, it can only from several:
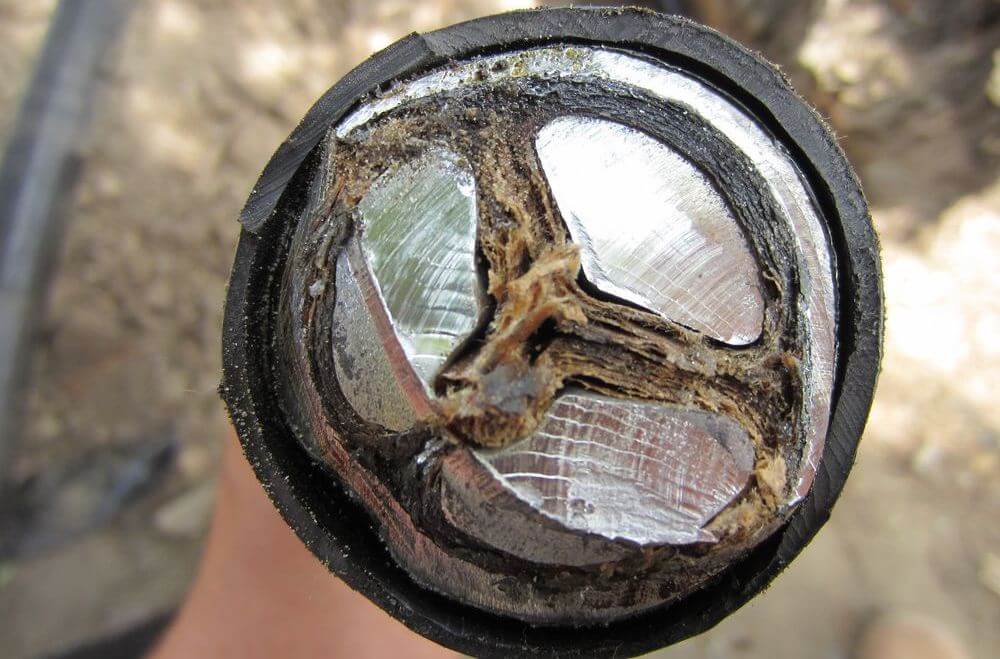
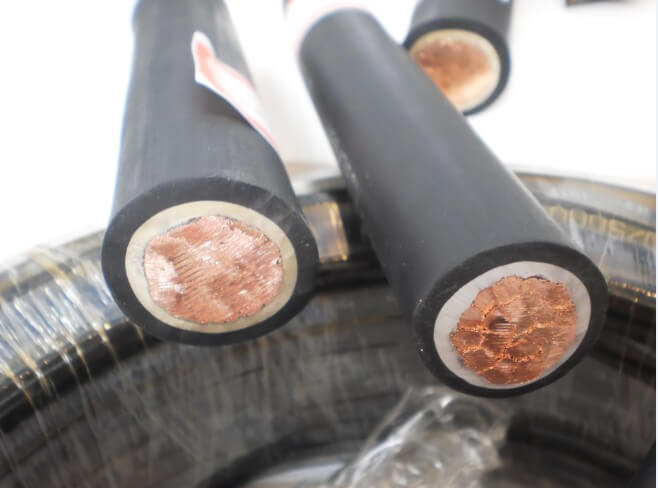
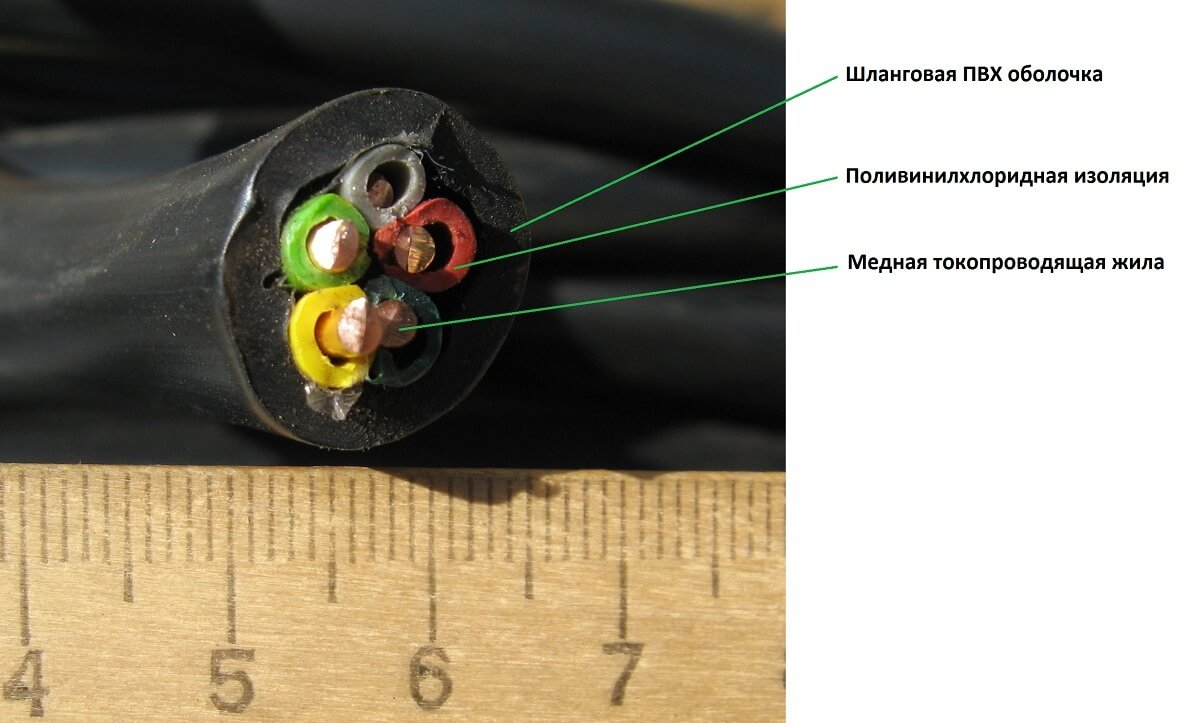
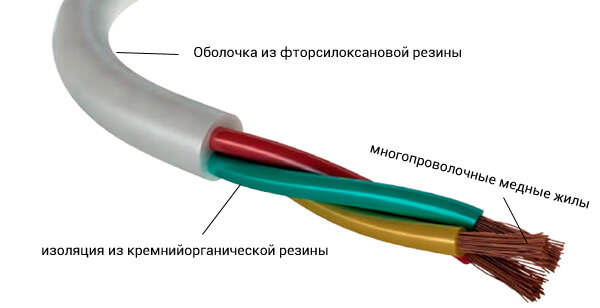
- Conducting vein. Serves for conducting current with the minimum possible heating. The main requirements for the veins: good flexibility, resistance to corrosion, high electrical conductivity and of course low cost.
- Insulation. A barrier that should provide the greatest possible resistance to electrical energy passing through the core. The insulating layer should have the highest possible dielectric properties, while in the largest possible temperature range. In addition, the insulation must be flexible.
- Screen. It is necessary to protect the conductive core from all kinds of external electromagnetic interference. The requirement for the design of the shielding layer is 100% insulation coating during bending.
- Belt insulation. Serves for additional protection of wires and cables from breakdown.
- Shell. Protects the conductor from mechanical damage, atmospheric phenomena, as well as moisture penetration.
- Protective cover. An additional sheath used in the operation of cable products in difficult conditions.
The construction of cables and wires consists of these individual elements. If you want to know more about the varieties and features of each component, a more detailed overview is provided below.
Parameter Overview
Conductive core
Veins of cables, wires and cords are made in accordance with current GOST 22483-2012, which in turn is a standard and determines the direct current resistance of 1 km of a core at a temperature of + 20 ° C. To identify electrical resistance, you need to know the cross section, the material of manufacture and the class of wire. We will consider each parameter in order, so that you understand how it affects the design of electric wires and cables.
The grade of wire can be from 1 to 6. The higher the grade, the better the flexibility of the conductor. For example, Grade 1 and 2 are used for the manufacture of cable products, which will be used exclusively for stationary laying. To connect mobile mechanisms you need to use cables with a flexibility class of 3 to 6.
As for the material of manufacture, this is a very important parameter.Copper conducts current better and is more resistant to mechanical damage. However, the disadvantages of copper wires are the higher cost and susceptibility to corrosion, especially at high humidity and temperature. Aluminum is cheaper and less susceptible to corrosion, but it is more fragile and forms an oxide film, which increases the contact resistance. Pros and cons of aluminum wiring We examined in a separate article.
Insulation
The insulating layer can be represented by the following materials:
- Polyvinyl Chloride Compound (PVC). The most common type of insulation, which at room temperature (+ 20 ° C) has a high resistance. The disadvantages of PVC compound are insufficient flexibility, when compared with rubber, and the fact that the insulation resistance of the wire is significantly reduced at a temperature of + 70 ° C and above. Advantages of PVC compound: low price, good resistance to many chemicals, moisture, and low flammability.

- Crosslinked Polyethylene (SPE). It is used for the manufacture of high-voltage cable products laid underground. The design of cross-linked polyethylene cables has good flexibility, low hygroscopicity (moisture absorption) and the possibility of heating to +130 ° C. The disadvantages of SPE cables are the complexity of manufacturing, the need to use foreign equipment, which is why the cost of the product is much higher than analogues.
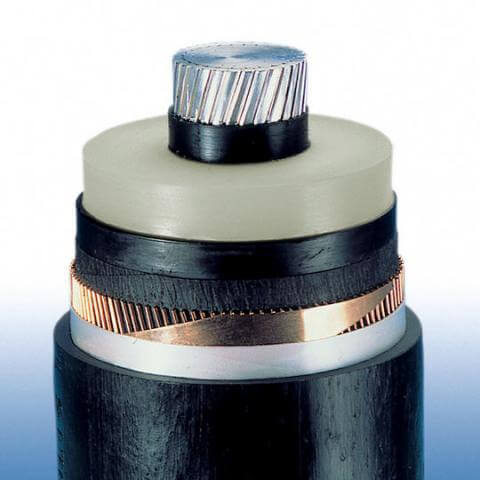

- Polyethylene. It can be low density (LDPE) and high (HDPE). Advantages: dielectric properties are 300 times higher than that of PVC insulation, low hygroscopicity, resistance to chemical reagents. However, the disadvantages of polyethylene are a decrease in the dielectric properties of the wire with increasing temperature, poor flexibility and at the same time high cost. The design of cables with polyethylene insulation is well established for laying stationary wiring in industrial facilities.
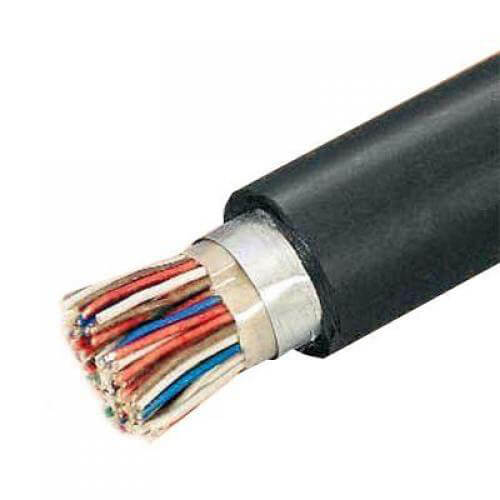

- Insulating rubber. Due to its flexibility, it is most often used to connect mobile mechanisms and equipment. Flexible, cheap, has high dielectric properties. However, it loses its electrical insulation characteristics at temperatures above +80 ° C, is susceptible to damage from ultraviolet radiation and, most importantly, it is not resistant to burning.
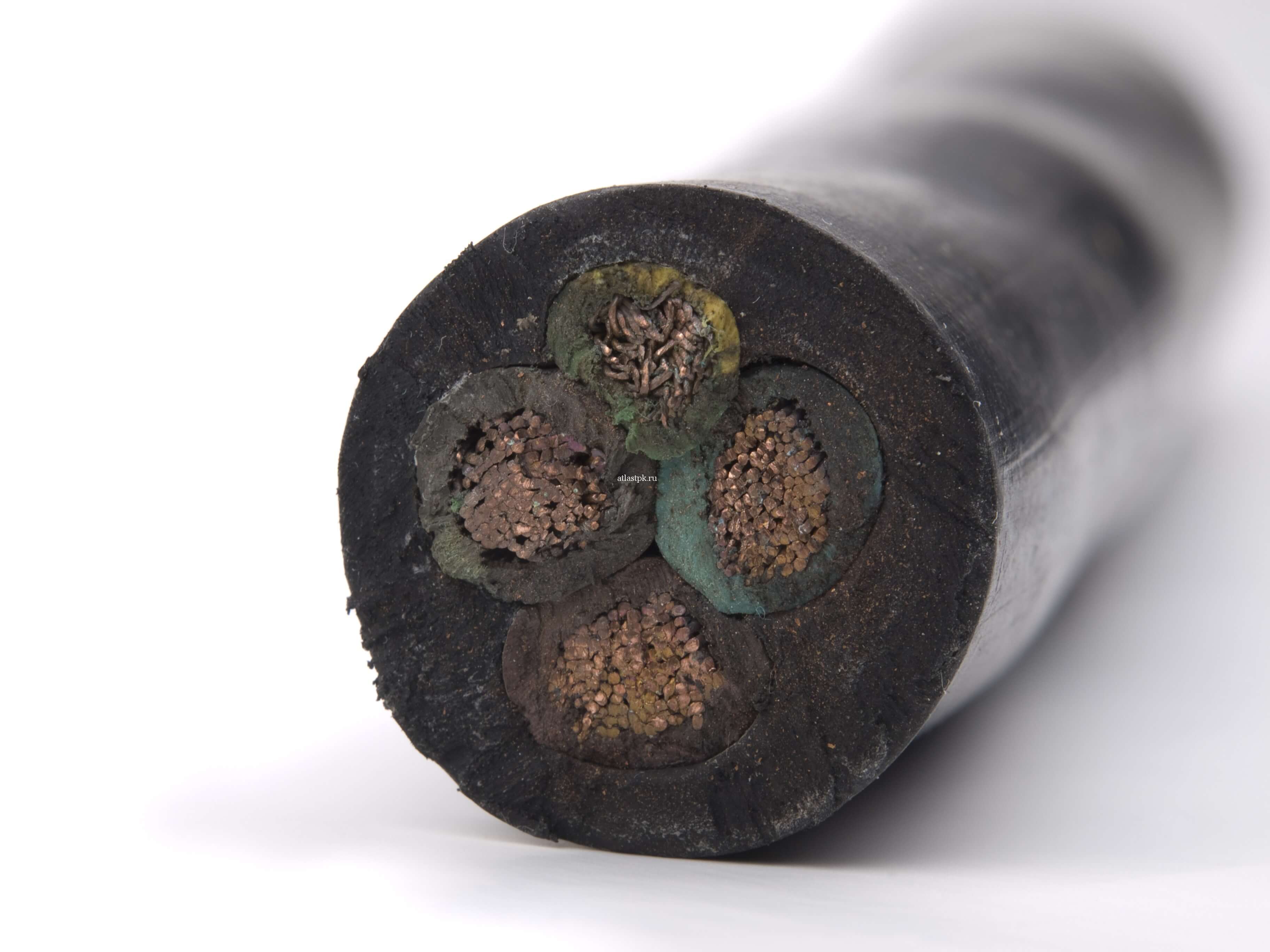

- Impregnated paper insulation (BPI). The design of paper-insulated cables consists of cable paper tapes impregnated with a special viscous or non-dripping compound. Requirements for the manufacture of this type of cable - paper tapes should not coincide when laying one on the other. No more than three matches or even two are allowed if the lowest tape is in contact with the shielding layer or the conductive core. The use of cables with BPI insulation - laying a high-voltage line in the ground. Advantages - low cost and high electrical insulation properties. Disadvantages - moisture absorption, high fire hazard, low resistance to mechanical damage and insulation fluidity with increasing temperature, which is why it is recommended to use a conductor exclusively for horizontal installation.

- Silicone rubber. It has high heat resistance, electrical insulation parameters, good strength and flexibility. At the same time, it is slightly resistant to chemicals, the design of the wire is destroyed during abrasion and is quite expensive. It is used, as a rule, in conditions with elevated temperature.
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). It has good resistance to mechanical damage even at temperatures up to + 250 ° C, while it is well resistant to chemical attack. The disadvantages of this type of protection are high cost and toxicity.
Screen
The next component in the construction of cables and wires is a shielding layer, the purpose of which is to protect the conductor from electromagnetic interference. Most often, the screen is used in control cables and high-voltage cable lines.
The main types of screens:
- from metallized paper (if the design provides for BPI isolation);
- copper wire (for PVC and rubber);
- galvanized steel wire (armor + crane);
- conductive rubber (with rubber type of insulation).
The shielding layer can be applied both to the entire bundle of cores, and to each separately. As a rule, it is flexible and additionally allows protect the wire from mechanical damage, however, due to the presence of a screen in the design, a running meter of the product will cost more.
Shell
This structural element of electric cables and wires protects against the negative effects of solar radiation, moisture, aggressive substances and of course mechanical damage.
For cable products with impregnated paper insulation, a lead or aluminum sheath is used. If the insulating layer is represented by PVC plastic or rubber, then the shell, respectively, can be either PVC or hose rubber.
The lead casing has good flexibility and resistance to chemical attack, it can be soldered in the field. The downside is that lead has a low melting point, so when exposed to heat and vibration, cracks can occur in the shell, up to a complete rupture. They struggle with these shortcomings by adding antimony and copper additives to the design.
Aluminum is more than 2 times stronger than lead, resistant to vibrations, and can act as armor and even a screen. The only bad thing is that the aluminum sheath of the cable has poor resistance to soil corrosion and also costs more.
PVC plastic compound is cheap, slightly damaged by chemicals, has mechanical strength and at the same time quite tight. However, it has poor flexibility, poor resistance to mechanical stress and light aging.
Hose rubber, in comparison with usual, well accepts tensile, shock and twisting loads. In addition, it can be resistant to oil, low temperatures and ignition. Disadvantages - is destroyed by the simultaneous exposure to oxygen and solar radiation, while poor resistance to chemical attack.
Protective cover
Well, the last element in the construction of cables and electric wires is a protective cover, which can consist of a pillow, an armor layer and an external cover.
The purpose of the pillow is additional protection of the insulating layer from damage by steel tapes or metal wire, which in turn represent armor. The pillow can be made of:
- crepe paper (has a high elongation to break);
- plastic tapes (alternative to crepe paper);
- bituminous composition (sticks together).
An armor layer is needed to protect the conductor structure from any kind of mechanical stress. Steel tapes do not absorb tensile forces and can be further protected against corrosion. In particular, two layers of steel tapes provide good protection against mechanical damage. The wire prevents strand twisting and works well in tension. It does not protect against mechanical damage.
Well, the outer cover should provide the cable with tightness, as well as resistance to various atmospheric phenomena. It can be represented by cable yarn made of fiberglass, additionally impregnated with bitumen or a cover made of plastic (PVC compound or polyethylene).
Typically, the specified outer cover may be included in the design of high-voltage cables with BPI insulation. Light outer coverings are inherent in wires: cotton yarn, fiberglass, sewing or linen thread.Also, the braid can be treated with an antifungal or weather-resistant compound or varnish in general, which will protect against moisture.
That's all we wanted to tell you about what a cable and wire consist of. Finally, we recommend watching a video in which all the individual structural elements are clearly demonstrated, the order of their placement:
As you can see, the design of wires and cables can be quite complicated, so it will not be difficult to choose the appropriate version of the conductor for your own conditions!
It will be interesting to read: