How to measure AC frequency?
What devices can be used
Frequency classification
All these devices are divided into two main groups according to their field of application:
- Electrical meters. Are applied to household or industrial measurement of frequency in alternating current circuits. They are used in the frequency adjustment of the speed of asynchronous motors, since the type of frequency measurement of speed, in this case, is the most effective and common.
- Radio metering. They are used exclusively in radio engineering and can measure a wide range of high-frequency voltage.
By design, the frequency meters are divided into panel, stationary and portable. Naturally, portable more compact, versatile and mobile devices that are widely used by radio amateurs.
For any type of frequency meter, the most important characteristics that, in principle, a person should pay attention to when buying are:
- The range of frequencies that the device can measure. When planning work with a standard industrial value of 50 Hz, you need to carefully read the instructions, since not all devices can see it.
- The operating voltage in the circuits in which the measurement work will take place.
- Sensitivity, this value is more important for RF devices.
- The error with which he can make measurements.
Multimeter with AC frequency measurement function
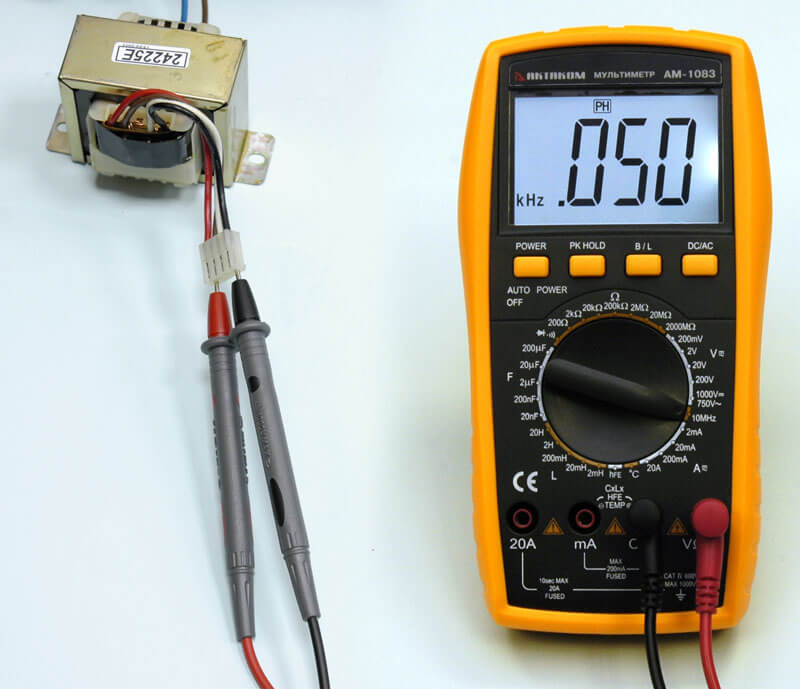
The most common device with which you can find out the magnitude of frequency fluctuations and which is freely available is a multimeter. It is necessary to pay attention to its functionality, since not every such device can measure the frequency of the alternating current in a socket or other electrical circuit.
Such a tester is most often very compact, so that it fits easily in the bag, and is as functional as possible, measuring voltage, current, resistance, and sometimes even air temperature, capacitance and inductance in addition to frequency. The modern look of the multimeter and its circuit are based purely on digital electronic elements, for a more accurate measurement. Such a multimeter consists of:
- A liquid crystal informative indicator for displaying the measurement results located, most often, in the upper part of the structure.
- The switch, basically, it is made in the form of a mechanical element that allows you to quickly switch from measuring some quantities to others. You need to be very careful, because, for example, if you measure the voltage, and the switch will be at the "I" mark, that is, the current strength, then the consequence of this will inevitably be short circuit, which will lead not only to failure of the device, but can also cause thermal burns by the arc of the person’s hands and face.
- Sockets for probes. With their help, an electrical connection of the device with a measured conductive object occurs directly. Wires should not have crackles or breaks in insulation, especially for their terminals, which will be in the hands of the measuring one.
I would also like to mention the special set-top boxes for the multimeter, which exist and are designed specifically to increase the number of functions of a conventional device with a standard set.
How is frequency measurement
Before using a multimeter, and in particular, a frequency meter, you need to carefully read again with those parameters that it has the ability to measure. In order to correctly measure them, you need to master several stages:
- Turn on the device with the corresponding button on the case, most often it is highlighted in bright color.
- Set the switch to measure AC frequency.
- Having picked up two probes and connected them, according to the instructions into the corresponding sockets, we will test the measuring device. First you need to try to find out the voltage frequency in a standard network of 220 volts, it should be 50 Hz (the deviation can be a few tenths). This value is clearly controlled by the supplier of electrical energy, as when it changes, electrical appliances can fail. The supplier is responsible for the quality of the electricity provided and strictly complies with all its parameters. By the way, this value is not standard in all countries. Having connected the conclusions of the frequency meter to the conclusions of the socket, a value of about 50 Hz will be displayed on the device. If the indicator is different, then this will be its error and in the next measurements it will need to be taken into account.
Further, you can safely make the necessary measurements, remembering that only the alternating type of voltage has a frequency, the direct current does not have a periodically changing value.
Other alternative measurement methods
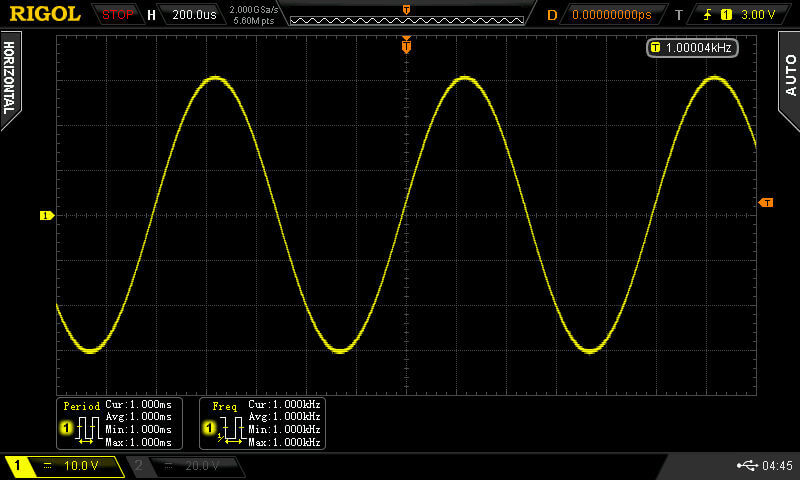
The most efficient and easiest way to check the frequency is to use an oscilloscope. It is an oscilloscope that all professional electronic engineers use, since on it you can visually see not only numbers, but also the diagram itself. In this case, it is necessary to disable the built-in generator. It will be quite difficult for a novice in electronics to perform measurement data with this instrument. About, how to use the oscilloscope, we told in a separate article.
The second option is to measure with a capacitor frequency meter having a measurement range of 10 Hz-1 MHz and an error of about 2%. It determines the average value of the discharge and charging current, which will be proportional to the frequency and is measured indirectly using a magnetoelectric ammeter, with a special scale.
Another method is called resonance and it is based on the phenomenon of resonance that occurs in the electrical circuit.Also has a scale with a fine adjustment mechanism. However, an industrial value of 50 Hz cannot be verified by this method; it works from 50,000 Hz.
You should also know that there is a frequency relay. Usually in enterprises, substations, power plants - this is the main device that controls the change in frequency. This relay acts on other protection and automation devices to maintain the frequency at the required level. There are different types of frequency relays with different functionalities, we will talk about this in other publications.
Nevertheless, multimeters and electronic digital frequency meters operate on a normal pulse count, which are an integral part of both pulsed and other alternating voltage, not necessarily sinusoidal for a certain period of time, while ensuring maximum accuracy as well as the widest range.
Finally, we recommend watching a useful video on the topic:
Now you know how to measure the current frequency in the network with a multimeter and a frequency meter. We hope the information provided was useful to you!
It will be interesting to read: