What are stray currents and how to get rid of them?
Causes
Modern life is impossible to imagine without electrified facilities. Energy consumption is growing every year, which entails the construction of new transformer and distribution substations, cable and overhead power lines, external contact networks for electric trains and contact rails for the metro. Since the earth itself is a conductor, and all these objects are on its surface or under it, a certain type of connection arises between them.
For an electric current to occur, a potential difference between two points of the conductor is necessary. The same statement is true for stray currents, except that the earth acts as a conductor in this case. In an isolated neutral system, the potential difference is provided by ground loops. If the neutral conductor is connected to the ground loop, its own resistance, when the charge passes through it, will cause a voltage drop. Such a conductor is designated PEN.
The base of the PEN conductor is connected to the ground circuit of the transformer substation. At the entrance to the consumer, it connects to the building memory. Both of these memories at opposite ends of the cable provide a potential difference, which, in turn, leads to the formation of stray current between them.
A similar process is observed when the insulation of power lines is damaged. If an earth fault occurs, then the earth in this area becomes the carrier of this potential. Most damage of this kind is repaired automatically. But this is in case there is a big leak. For small values, localizing and neutralizing the cause is rather problematic.
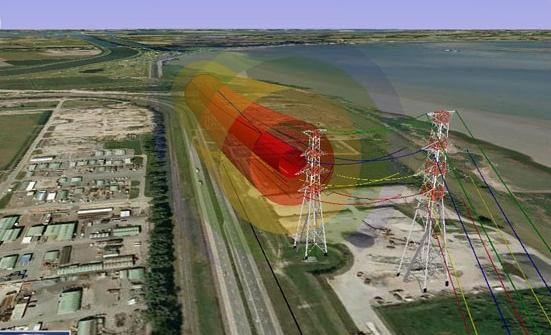
Vehicles powered by electric traction (with the exception of cars that operate using autonomous electric motors) are the main cause of this undesirable phenomenon. Trolleybuses are connected to the electric network by means of special rods that are connected to the neutral and phase wires and are located on the vehicle itself. Therefore, this type of transport does not generate large stray currents.
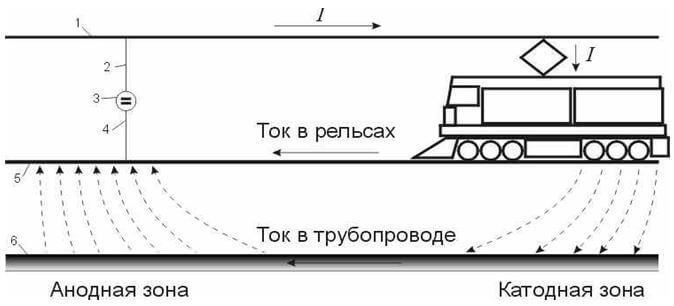
Electric trains are powered by a slightly different principle. The zero conductor is connected to the rails, and the phase conductor is mounted above the tracks.With the help of pantographs located on the roof and directly in contact with the power cable, electricity is supplied to the engine.
Power supply to these networks is provided by traction substations, which are located along the entire route at approximately the same distance from each other. The main cause of stray currents in this system is the curvature of the route. An electric charge passes along the path of least resistance. Accordingly, if the opportunity arises to “cut corners,” he will walk on the ground, and not on rails.
The video below details what this phenomenon is and how it occurs:
Impact on metal objects
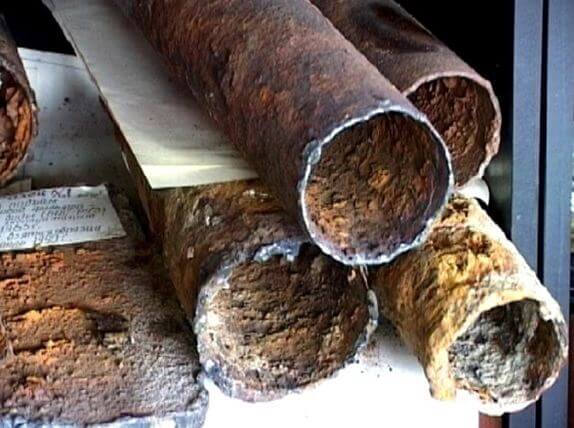
There are many metal objects in the earth, such as: various piping systems, armored cable lines, reinforced concrete foundations of buildings. Since metal is a better conductor compared to earth, the electric current will pass through it, and not through the ground. The entry point is called the “cathode zone”. The exit point is the “anode zone”.
Separately, I would like to consider the corrosion processes in water pipes. Groundwater contains many soluble substances and is a good conductor. For example, in a pipeline in the ground, corrosion forms as a result of the electrolysis process. This is especially pronounced in the area of the anode zone. Structures in the cathode zone are less destructive.
As a result of the extremely destructive effect on all of the above objects, wandering currents can cause significant economic damage.
Protection methods
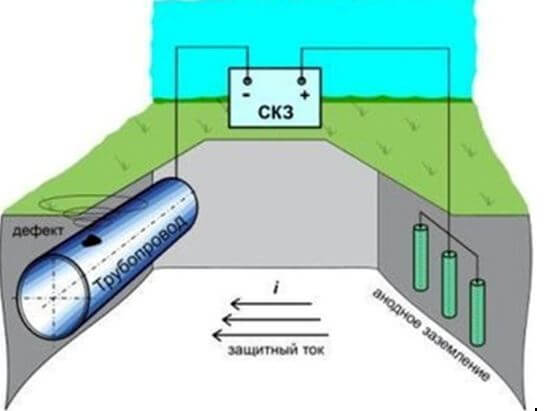
The most common way to deal with this phenomenon is to install cathodic protection. To do this, it is necessary to exclude the formation of the anode zone on the protected structure and leave only the cathode. The cathodic protection station generates direct current, connecting the negative pole to the metal structure that needs to be protected, and the positive one to the so-called "sacrificial" anodes, which take on the bulk of the destructive force. Also, special protective coatings that prevent the formation of a corrosion layer are applied to the protected object.
VHC Scheme:
The disadvantages of this scheme are:
- the so-called "rebuild" - when the protective potential is exceeded and the protected metal structure is corroded;
- incorrect calculation of protection, in which accelerated corrosion damage occurs near located metal objects.
Unfortunately, this problem affects not only industrial facilities, but also ordinary people. In the heated towel rail, as in the heating system as a whole, hot water circulates, which is an excellent conductor (unless, of course, it is not distilled). If the pipelines and the adjacent elements that are in the living room are not properly grounded, then they may be susceptible to the appearance of an undesirable potential and, accordingly, rust spots on their surface. Proper grounding will help prevent all these negative consequences, so today this method of protection against stray currents in an apartment and a private house is one of the most effective.
Measurement methods
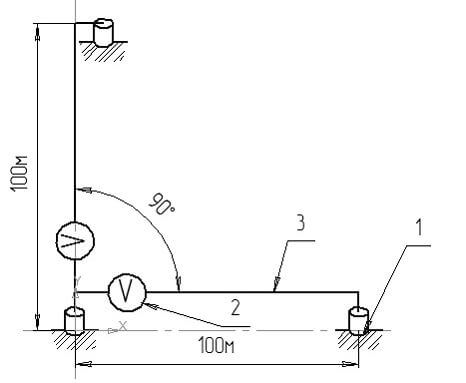
When laying a pipeline, stray currents are calculated by measuring the potential difference between two points of the earth's surface, perpendicular to each other and at an equal distance of 100 m. Measurements are made every kilometer.
Measuring instruments must have an accuracy class of at least 1.5 and their own resistance of 1 MΩ. The potential difference between the measuring electrodes should not exceed 10 mV. In time, one measurement should last at least 10 minutes, with the result being recorded every 10 seconds.
Measurements in the area of electric transport must be carried out during the greatest load.If the potential difference of the readings exceeds 0.04V, then this is a sign of the presence of stray currents.
As measuring instruments, a pair of reference electrodes can be used: copper-sulfate portable and connecting. In addition, you will need a digital multimeter to take measurements, as well as a flexible insulated wire, the length of which should be at least 100 meters.
Despite its small values, this phenomenon can cause significant damage to underground (and not only) communications. Sources of stray currents can be very different. Therefore, it is necessary to take all preventive measures to eliminate this undesirable effect.
Finally, we recommend watching a useful video, which clearly shows how to protect yourself from this phenomenon:
So we examined the causes of stray currents and protection against them. Now you know what it is and how to get rid of this phenomenon even at home!
Surely you do not know: