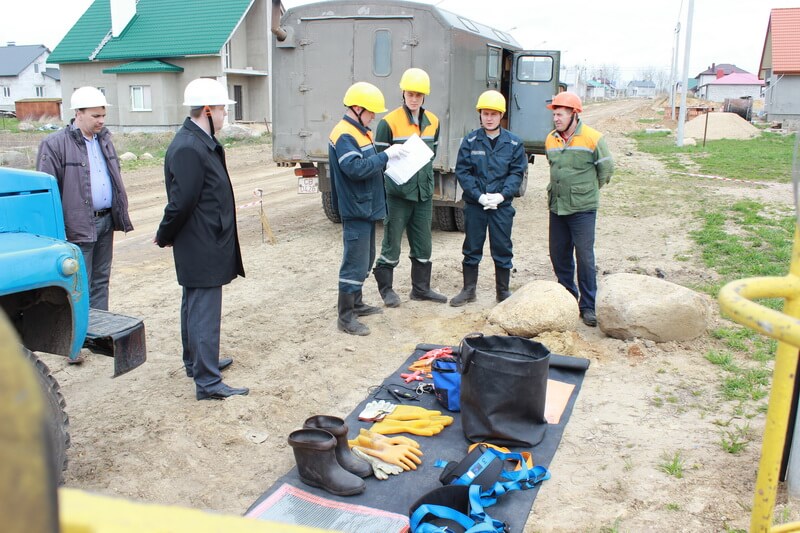
Protective measures for live work
Protection methods
In order to bring these parts of electrical installations, it will take a lot of effort, also, it can be difficult if it is an important high-voltage line and there is no way to turn it off. That is why work under stress is a developing and improving modern technology for servicing power systems that significantly speeds up the troubleshooting process.
There are several ways to work near live objects. Certain means of protecting the worker from electric shock correspond to each method. Next, we will consider three of them.
Isolation of the worker from the ground
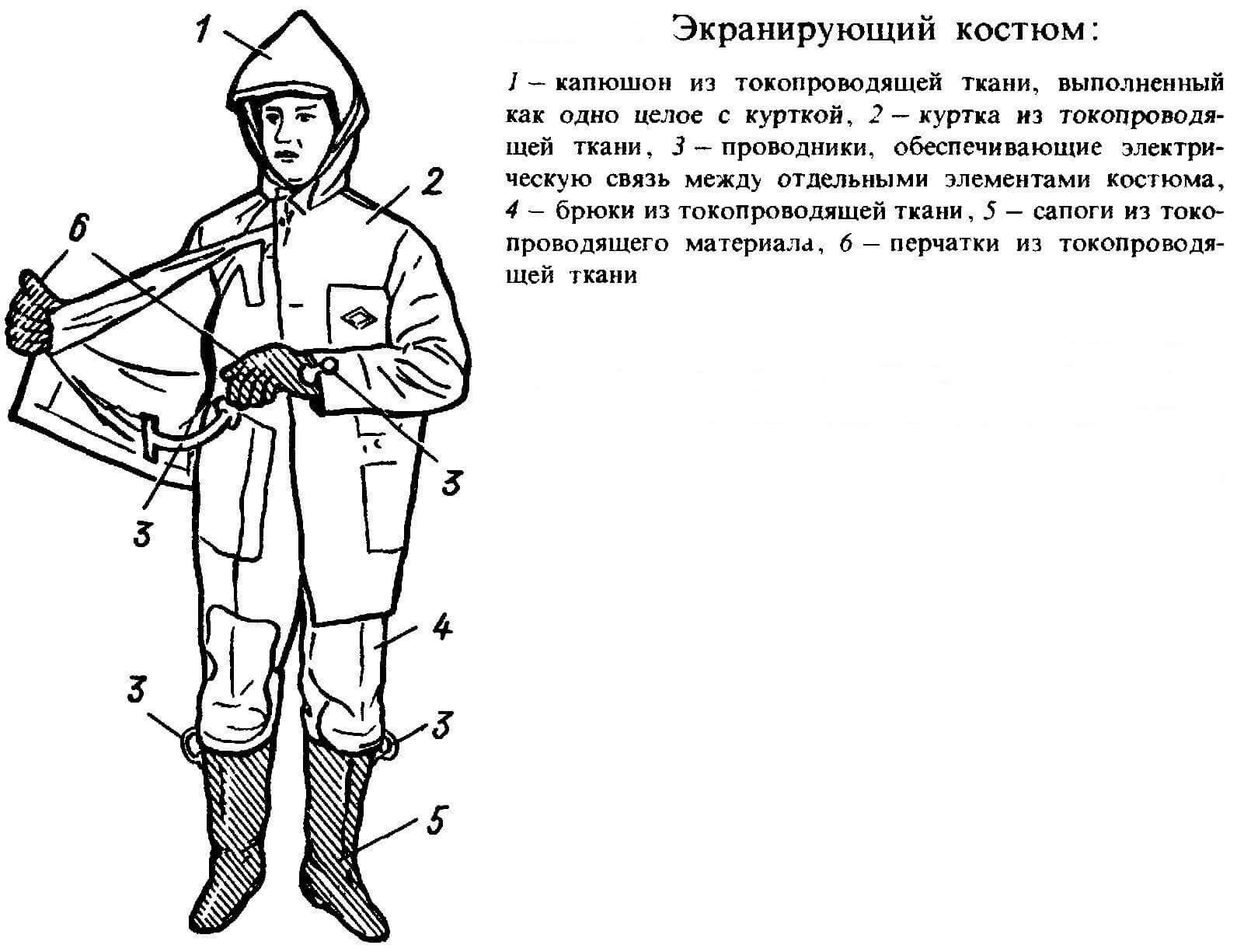
In this case, the work is carried out under voltage, as well as under the potential of the wire. The work of a worker standing on an isolated site using special equipment here is a methodology for working under load. His suit is designed in such a way that an isolated stand is easily connected to it.
Before starting repairs, you must first align the potentials of the work stand and shielding suit with de-energized live parts. Alignment is carried out by connecting an isolated area and a current-carrying area thanks to a copper conductor.
Current-carrying sections with grounded parts of metal structures likewise have a potential difference. Because of this, the worker is strictly forbidden to approach them at a distance that exceeds the permissible norms for this class of line voltage. Otherwise, the worker may be seriously damaged by electric shock. For example, a worker is forbidden to approach metal structures closer than 2 and a half meters when working in 330 kV distribution networks.
Each employee must undergo special training and testing for knowledge of the technology for carrying out work according to this method, since this is a big risk. For the planning of the workflow, special technological maps are compiled, as well as special instructions.
Isolation of the worker from conductive areas without isolating from the ground
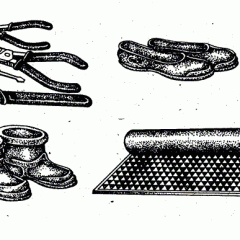
With this method, the use of special electrical protective equipment is mandatory. They are selected based on the nature of the work and the voltage class of the electrical installation. There are basic and additional electrical protective equipment for working with voltages up to 1000 volts and higher.
Basic protective equipment allows working for some time under load. They protect the worker from the influence of the arc and electrical voltage in the area of the electrical installation.
The use of additional protective equipment is intended only for auxiliary protection in addition to the basic ones. Thanks to them, it is impossible to work under load, they are able to protect only from touch voltage and step voltage. This method of work is perhaps the most commonly used in electrical installations.
For clarity, we give an example:
Checking the voltage indicator in electrical installations above 1 kV. The main insulating agent is this pointer, and it is necessary to use it only with the use of dielectric gloves. In this example, they will constitute an additional protective agent.
Isolation of the worker from live parts and earth
The most popular example is the implementation of electrical work in a network under a voltage of up to 1000 volts. These include distribution boards as well as cabinets relay protection and automation.
In this method, protective devices ensure reliable safety of the worker from electric shock. Dielectric gloves and such tools with insulating handles as nippers, screwdrivers, pliers, etc., are used to isolate the worker, and in such electrical installations where the voltage reaches 1000 volts, they are the main means of protection against electric shock. There are also additional tools for isolation from the ground, namely a dielectric mat and an insulating stand.
Visual instructions
Finally, we recommend that you watch the video, which provides general information about the work under high voltage:
And here is how they do it in the USA:
Now you know how live work is done and what safety measures personnel need to take. Take care of yourself!
We also recommend reading: