Which wire is better: single or stranded
What a wire or cable consists of
The wire and cable within this article do not have significant differences, so we omit them and equate these concepts. They consist of a conductive core bare or coated with one or two layers of insulation. The insulation is made of a dielectric material, for example, PVC, rubber, polyethylene, fluoroplastic. The cores are made of aluminum or copper. Also, according to the structure of the vein, there are:
- Single wire - rigid. They consist of a solid cylindrical or shaped (sector) conductor, sometimes they are called monolithic.

- Stranded - soft. Consist of 7 or more thin wires. The exact number of wires is determined in the technical specifications for the product and in GOST 22483-2012, it depends on the cross-sectional area of the TPG and its flexibility class.

Interesting! As we have already said, the correct names for the types of cores are precisely single-wire and multi-wire, but they are often referred to as single-core and multi-core. Therefore, sometimes confusion arises when they speak of a stranded wire: is it the number of conductive wires (more than one), or the number of wires in one core? Within this article, take these concepts as synonyms.
Flexibility class
Single and multi-wire wires are flexible. This concept characterizes the ability of a cable to bend without damage. Only 6 classes of flexibility, where 1 is the toughest and 6 is the most flexible.
For example, a solid wire PV-1 - flexibility class 1, and for a wire with a soft multi-wire core PV-4 - flexibility class 4. In this particular case, the flexibility class is laid down in the marking.
In the figure below you can see the difference in the structure of cable cores of different flexibility classes. You can make sure that cables with a flexibility class of more than 2 multicore, and the larger the class, the more veins.
Choose between solid and stranded wire
On the example of specific situations and devices, we consider which particular wire is better: single-core or multi-core.
In general, stranded wires are better suited for powering non-stationary or mobile electrical equipment. When stationary laying they are conveniently laid in cable channels, they more easily pass turns and bends.
For wiring in the house and laying in the gate, single-core cables are better suited.They withstand large mechanical loads such as squeezing and stretching, and mobility with this method of laying is completely unnecessary.
In the shield with automatic machines and RCDs, it is easier and better to conduct single-wire insulated wires of the PV-1 type. So they will be firmly in place, will not break if accidentally jerked, for example, when replacing the machine. Plus, such wires will firmly hold the shape that you give them.
Single-wire and multi-core wires can be used in the control panel (control panel) depending on the type of terminals on the installed equipment, as well as on the number and location of the equipment. Shields should provide convenient and expeditious maintenance not only by their design, but also by the internal installation of equipment.
In information networks, for example, for video surveillance, telephony, and the Internet, special cables with single-wire core are usually used, and multicore conductors are used to power these devices. Or they feed directly on the communication cable.
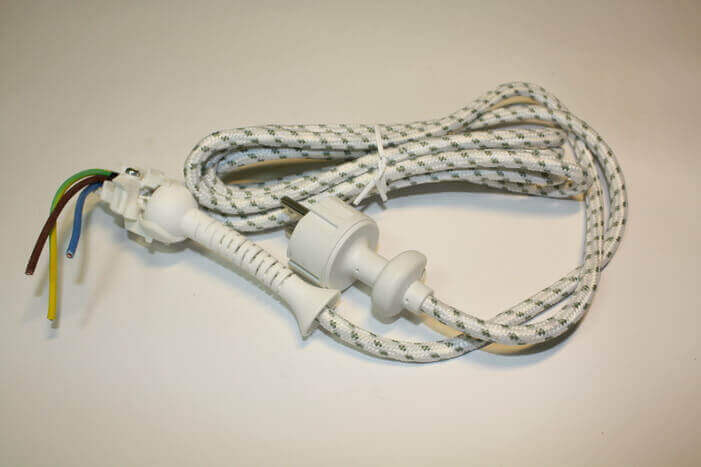
Cords are used for mobile equipment, for example, drills and other power tools, irons, table lamps. In irons, the cord is covered with a fabric braid, for additional protection against high temperature and friction.
Frequently asked question: what holds current better? In a household electrical network with a frequency of 50 Hz, the number of wires in the core does not have special values. The choice of wire is based only on the installation and operation conditions described above.
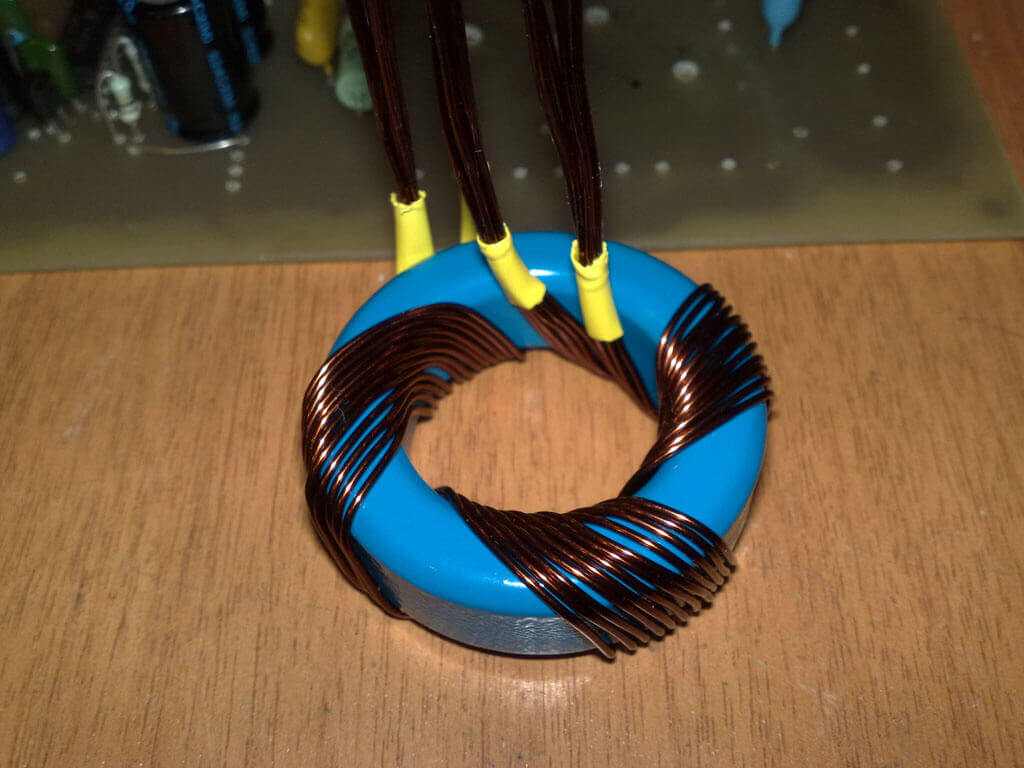
In high-frequency circuits and in sound equipment, as well as in acoustics, a skin effect takes place. This phenomenon is when the current flows to a greater extent along the surface of the cable, and the higher the frequency, the more charge carriers are pushed to the surface.
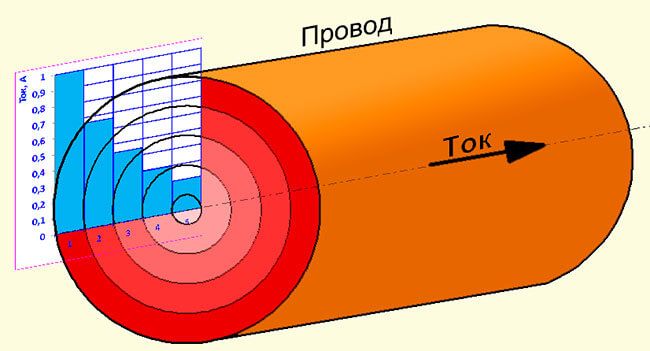 This causes a decrease in the useful cross-sectional area, therefore, an increase in cable losses. Therefore, either braided individual single-wire conductors (in high-power pulse transformers) or soft multi-wire conductors are used.
This causes a decrease in the useful cross-sectional area, therefore, an increase in cable losses. Therefore, either braided individual single-wire conductors (in high-power pulse transformers) or soft multi-wire conductors are used.
The article considers the main areas of application of cables in everyday life. We can briefly say this: the choice of a wire with a single-wire or multi-wire core depends only on the specific situation and operating conditions of the equipment, its mobility. If in doubt about which wire to use: single-core or multi-core, ask in the comments, we will try to help you.
Finally, we recommend watching a useful video on the topic of the article:
Also read:

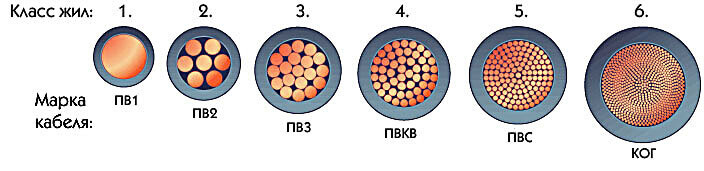










If my memory serves me, a wire of seven veins is called a small-core, more than seven many-core, and with one mono.