How to lay the cable in cable ducts and what requirements need to be considered
What is cable drainage and how is it arranged
Cable sewage is an underground method for laying cable lines in a structure consisting of channels (pipes) and wells for their inspection and maintenance.
A distinctive feature of cable laying in cable ducts is the possibility of replacing old and laying new lines without carrying out earthwork, that is, through the channels available in it using underground pulling.
The technology of laying the line is that the end of the cable is lowered into the well, and then pulled into the existing channels manually or using special mechanisms. The cables themselves are often laid in a single piece equal to its construction length, that is, without unnecessary connections in transit pass through intermediate wells.
In this way, it is possible to lay both power cables and communication cables, such as a telephone network or FOCL, they are also fiber-optic lines, they are used for data transmission (for example, the Internet, television, telephone communication). However, the power cable cannot be located in the same pipe with the communication cable (This is indicated by the rules of the PUE, namely chapter 2.1. paragraph 2.1.16, chapter 2.3. paragraph 2.3.86 and other documents, for example, BCH 116-93 p. 6.3., P. 8.2 and other more modern).
The distance between the wells of cable ducts depends on the location of the sewer itself and the type of cables laid in it, and can be quite large (from 25 to 150 meters). The depth of the pipe depends on the load on the soil and its type, usually lies in the range of 40-200 cm. That is, under the road they lay at a greater depth, where there are no roads - at a smaller one.
In this case, the slope of the pipe should be maintained on the order of 3-4 mm per meter (so that moisture does not accumulate). The pipes themselves are laid in a straight line, only a small displacement is permissible, no more than 10 mm per 1 m of length. In the modern world, various polymer pipes (for example, polyethylene) are more often used, and in old cable ducts - metal or asbestos-cement. The inner diameter of the pipes usually does not exceed 100 mm.
As for the wells, they have different names, depending on their location and purpose:
- if they are located on a straight section, with a deviation of not more than 30 mm - they are called walk-through;
- near the building - an inspection manhole;
- if located on a sharp turn or bend of the line, then this is a rotary well;
- if in this place several channels converge or diverge and are connected in one well, then they are dividing.
How to lay the cable
There are different ways of laying the cable, associated with the design features of both the cable itself and the sewage system in which it is laid. However, in general, cable installation in cable ducts can be divided into several stages:
- Before starting work, check for gas accumulation in the well. If the work is not dangerous, then start by checking the cable channels.
- Check the integrity of the channel using cable poles. Cable sticks are duralumin sections of about 1 m long with threaded connections (stud and internal thread) at the ends. They are screwed onto each other and pushed into the channel until the tip of the stick appears at the end of the span (in another well).
- During the check, determine the condition of the channel (check the integrity and throughput of the pipes). For example, if one of the pipes of the channel sags, it will complicate the further cable laying.
- If the channel is clogged, then the blockages are cleaned with a special metal scoop mounted on the end of the sticks, feeding it into the channel and rotating it. The remains of garbage are cleaned with a brush, in the same way.
- These operations are carried out until the end of the stick comes out in the next well. What other workers report from the next well through the canal.
- After checking and cleaning the channel proceed to laying the cable.
- The sticks are removed from the pipe after first securing a broach at their end from the distant well to tighten it into the well from which the cable will go.
- Depending on the type of product, laying methods are chosen, for example, a telephone cable up to 100 pairs is pushed through the channels manually. More - with the help of mechanical devices (for example, winches).
- Before broaching, the ends of the cable are sealed so as not to damage it, and pulled by the sheath and the power central element. To do this, use a special stocking, is a mesh or spiral that wraps around the end of the cable (see video below). It is attached to the broach before being introduced into the channel.
- After that, the cable is pulled from the second well and fed from the first.
- If any of the sections passes in the basement or through other underground structures, in this case, consoles are used to lay the cable, and lines are placed along the walls.
- The pipe for laying the cable in the cable duct is not just chosen so that the higher the voltage on it, the lower it should be located.
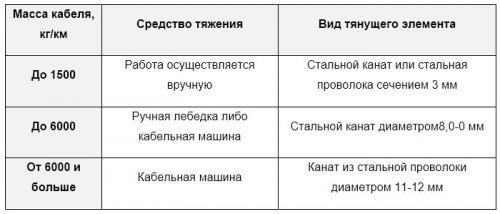
The table below shows the norms for choosing a method for pulling a cable line through cable ducts:
The set of equipment, as already noted, will differ depending on the installation features and the type of cable product, we present one of the typical options:
- universal winch;
- UZK;
- flexible guide tube for introducing cable into the manhole;
- wires and cables;
- spacers and blocks, for turning the line, turning in corner wells;
- funnels, to protect when immersed in the well and create the desired bending radius;
- stocking;
- torsion compensator to compensate for axial torsion.
Based on the foregoing, the following answer can be given - it is impossible to lay the cable in the cable duct with your own hands in any way, because you need a set of tools and permission to carry out such work. The installation of underground lines in this way should be carried out by an organization on the balance of which there is a specific sewage system, or an organization that has permission and access to it.
Normative documents: GOSTs, SP, SNiPs
There are several regulatory documents that establish the rules for laying cables in cable ducts:
- Individual items in PUE, for example, in chapters 2.1, 2.3, which were given at the beginning of the article.
- Code of Practice 76.13330.2012 (this is an updated version of SNiP 3.05.06-85) which describes the requirements for the development of design documentation (section 6.4.2.“Laying in a pipe block sewer”), this is reflected in more detail in the old SNiP.
- BCH 116-93 (Instruction for the design of linear-cable communication facilities), but it was canceled since 2003, and nothing was accepted in exchange, and therefore specific profile enterprises have internal requirements (for example, Giprosvyaz OJSC - “Design Instructions” of linear cable communication facilities ”2005 or JSC“ Rostelecom ”“ Main technical requirements and norms for the construction of cable crossings through water barriers using a trenchless method at the facilities of JSC “Rostelecom”).
- GOST R 50889-96 “Structures of local telephone networks are linear. Terms and Definitions".
- OSTN-600-93 “Industry-specific building and technological standards for the installation of communication and broadcasting and television facilities and devices” (but also canceled together with BCH 116-93).
The canceled documents were distributed among a number of other documents, where the norms and requirements for cable laying in cable ducts are described in separate paragraphs, the list can still be continued, but we selected the most frequently used documents.
In the end, we recommend watching useful videos on the topic of the article:
Related materials: