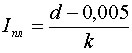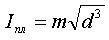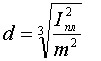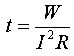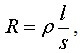Fuse Calculator Calculator
To protect electrical circuits from emergency operation, such as increased power consumption or short circuit, use fuses or fuses. They are arranged in such a way that when a current flows to a certain level, nothing happens, but, according to Joule-Lenz law when electric current flows, heat is released on the conductor. Therefore, with a certain amount of heat current, such an amount is released that the fuse-link conductor simply burns out.
In electronic circuits, fuses are installed at the power input, it is needed to protect the transformer, circuit board tracks and other nodes. It is also used to protect the electric motor - they are often installed in the shields to which they are connected. For example, when the rotor of the electric motor jams in the stator circuit (and the rotor too, for DPT, and motors with a phase rotor), an increased current will flow, which will burn the fuse. But if its value is selected excessively large, then the windings of the electric machine will burn.
In addition to the conductor itself, the fuse consists of a glass or ceramic case, and for high power and voltage, the case is filled inside with a dielectric powder material - this is necessary to extinguish the arc that occurs when a fuse is burned out.
It would seem that a simple device and principle of operation, but for its calculations, you need to use a number of formulas, which greatly complicates the task. Although you can avoid them, if you use our online calculator, which calculates the fuse insert:
Let's figure out how to calculate the diameter of the wire. To begin with, they determine Inom of the consumption of the protected device. It can be found out from the technical documentation, for electric motors - read on the nameplate or determined by the power of the device. If the parameter is not specified, define it using the formula:
Inom = P / U
After this, calculations are performed on the current multiplied by the safety factor, which is 1.2-2.0, depending on the type of load and its features. With the existing thin wire of a certain diameter, Imelting is calculated:
With wire diameters from 0.02 to 0.2 mm:
From 0.2 mm and above:
Where:
- d is the diameter;
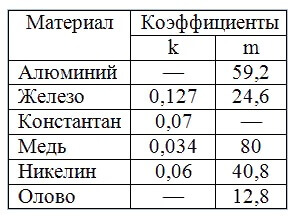
- k or m is the coefficient; it is given in the table for various metals.
To determine the diameter of the wire knowing the current I:
For small I - d from 0.02 to 0.2 mm:
For large I, the wire diameter is from 0.2 mm and above:
If you need to know the amount of heat that is released on the fuse box, then use the formula:
The time and amount of heat for melting:
Where:
- m is the mass of the wire;
- Lambda - specific amount of melting spot, tabular value characteristic for each material.
Mass of round wire:
To check the correctness of the calculations, you can measure the resistance of the conductor according to the formula:
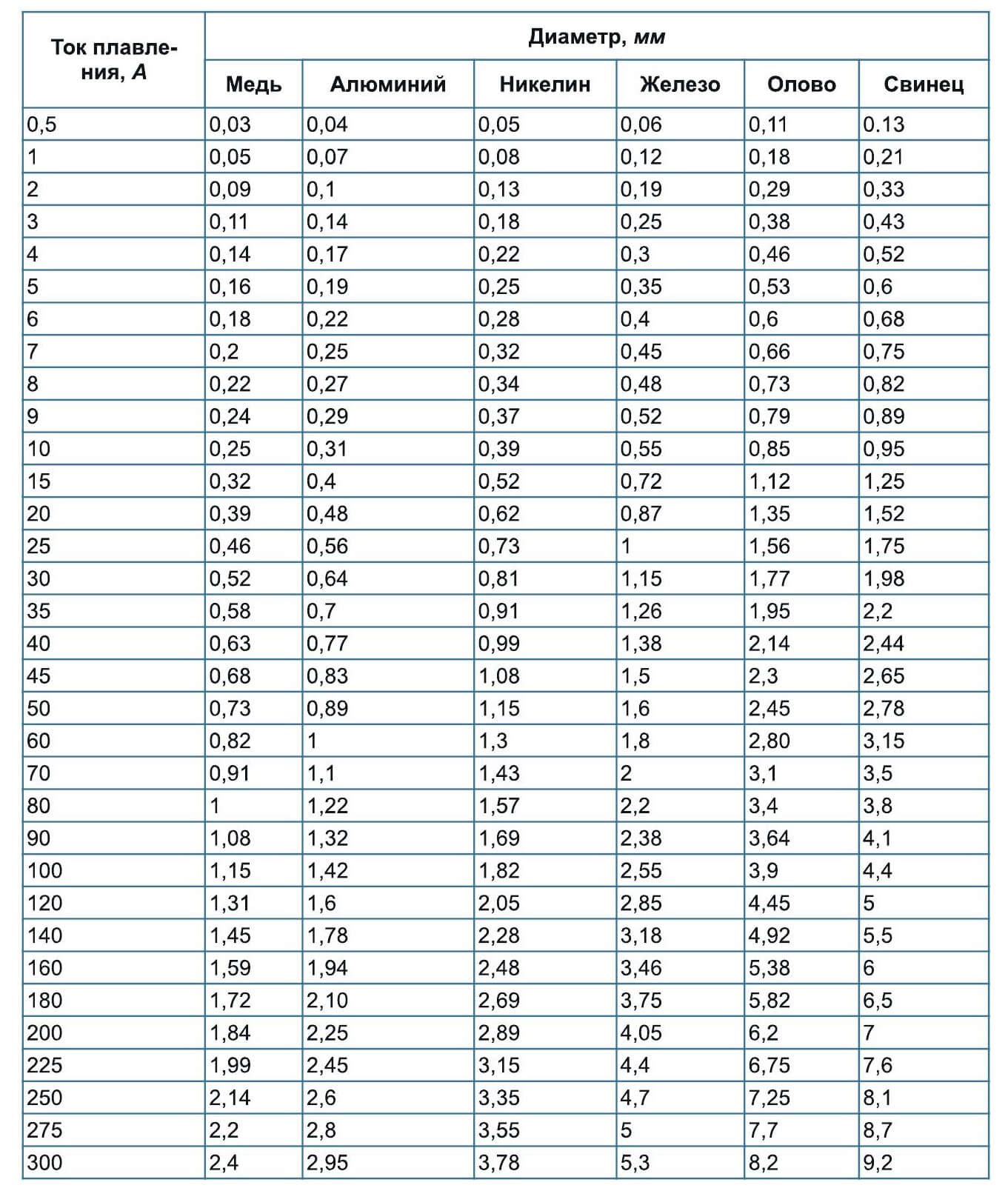
By the way, fuses of high voltage circuits usually have a high resistance (kilo ohms).For convenience, you can use the table:
As you can see, the calculation of the fuse insert is quite voluminous, so it’s easier to calculate the protective fuse using our online current calculator. As already mentioned, you can determine it based on power.